Proff P, Romer P: The molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: a review. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ: Cancer Statistics, 2007. 2003, 3: 537-549. 10.1210/er.19.1.18. NF-B/MAP-kinase inhibitors (SN50, PD98059 and SB203580), COX-2 inhibitors (indomethacin) and EP4 receptor decoy [46] all result in a down-regulation of RANKL production and a concomitant decrease in osteoclastogenesis. H Singh and JA Neutze (eds. This is called osteolytic metastasis. Yang Y, Ren Y, Ramani VC, Nan L, Suva LJ, Sanderson RD: Heparanase enhances local and systemic osteolysis in multiple myeloma by upregulating the expression and secretion of RANKL. 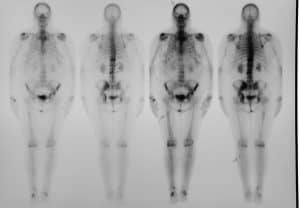 Several groups have developed in vivo models in which bone or bone substitutes are implanted in animals. Standal T, Borset M, Sundan A: Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone remodeling. These cells fuse to form multinucleated, but non-functional pre-osteoclasts. Mixed lesions In the majority of skeletal metastases, new bone develops simultaneously with bone destruction. The roentgenogram indicates the net effect of these two processes. Where the bone formation predominates, the lesion appears sclerotic. Where bone destruction predominates, it appears lytic. Drugs of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years as the standard of care. Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the roles of MMPs. Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordon-Cardo C, Guise TA, Massague J: A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)02937-6. To date, osteoclasts have been the primary target of drug therapies. However, cathepsin K is also produced by other cells in the bone microenvironment, such as macrophages and bone marrow stromal cells. 10.1016/S8756-3282(03)00086-3. Pozzi S, Vallet S, Mukherjee S, Cirstea D, Vaghela N, Santo L, Rosen E, Ikeda H, Okawa Y, Kiziltepe T, Schoonmaker J, Xie W, Hideshima T, Weller E, Bouxsein ML, Munshi NC, Anderson KC, Raje N: High-dose zoledronic acid impacts bone remodeling with effects on osteoblastic lineage and bone mechanical properties. 7, Chapter Recently, Roy and colleagues [69] investigated this association in a mouse model of autoimmune arthritis and found that arthritic mice had an increase in both lung and bone metastasis compared to the non-arthritic mice. Google Scholar. At higher doses they may in fact prevent osteoblast differentiation [30]. MMP-9 is important in the cascade leading to activation of VEGFA. 2010, 87: 401-406. Cells of the osteoblast lineage are derived from mesenchymal stem cells, and are represented in this unit by osteoblasts, bone lining cells and osteocytes. PubMed WebWhen cancer cells spread to the bones (bone metastases), they can cause many problems such as pain, broken bones, or more serious problems. Osteoblasts derive from mesenchymal stem cells in the marrow under control of Runx2, a key osteoblastic transcription factor. Trabecular bone is the major site of bone turnover under normal conditions and in diseases of bone loss or formation. There are two types of lesions: lytic lesions, which destroy bone material; and blastic lesions, which fill the Phadke PA, Mercer RR, Harms JF, Jia Y, Frost AR, Jewell JL, Bussard KM, Nelson S, Moore C, Kappes JC, Gay CV, Mastro AM, Welch DR: Kinetics of metastatic breast cancer cell trafficking in bone. There are many suspected factors, such as microfractures, loss of mechanical loading, hormones, cytokines, calcium levels and inflammation. Bone metastasis significantly affects both quality of life and survival of the breast cancer patient. A lytic lesion describes an area of bone damage that often appears as a hole. Denosumab (Prolia), the latest drug to enter the field, is a monoclonal antibody to RANKL. Denosumab has recently been approved by the FDA for treatment of osteoporosis in women with high risk of fractures and is being considered for treatment of bone metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. It is estimated that 85% of individuals with advanced disease harbor bone metastases [1]. In the bone, OPN is involved in the differentiation and activity of osteoclasts, and inhibition of mineral deposition in the osteoid [37]. Once osteoblasts finish bone deposition, they undergo apoptosis, remain in the matrix as osteocytes or revert to thin bone-lining cells. There is evidence in both humans and animals that bone loss in osteolytic metastasis is partly due to the failure of the osteoblasts to produce new osteoid for the bone matrix.
Several groups have developed in vivo models in which bone or bone substitutes are implanted in animals. Standal T, Borset M, Sundan A: Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone remodeling. These cells fuse to form multinucleated, but non-functional pre-osteoclasts. Mixed lesions In the majority of skeletal metastases, new bone develops simultaneously with bone destruction. The roentgenogram indicates the net effect of these two processes. Where the bone formation predominates, the lesion appears sclerotic. Where bone destruction predominates, it appears lytic. Drugs of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years as the standard of care. Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the roles of MMPs. Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordon-Cardo C, Guise TA, Massague J: A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)02937-6. To date, osteoclasts have been the primary target of drug therapies. However, cathepsin K is also produced by other cells in the bone microenvironment, such as macrophages and bone marrow stromal cells. 10.1016/S8756-3282(03)00086-3. Pozzi S, Vallet S, Mukherjee S, Cirstea D, Vaghela N, Santo L, Rosen E, Ikeda H, Okawa Y, Kiziltepe T, Schoonmaker J, Xie W, Hideshima T, Weller E, Bouxsein ML, Munshi NC, Anderson KC, Raje N: High-dose zoledronic acid impacts bone remodeling with effects on osteoblastic lineage and bone mechanical properties. 7, Chapter Recently, Roy and colleagues [69] investigated this association in a mouse model of autoimmune arthritis and found that arthritic mice had an increase in both lung and bone metastasis compared to the non-arthritic mice. Google Scholar. At higher doses they may in fact prevent osteoblast differentiation [30]. MMP-9 is important in the cascade leading to activation of VEGFA. 2010, 87: 401-406. Cells of the osteoblast lineage are derived from mesenchymal stem cells, and are represented in this unit by osteoblasts, bone lining cells and osteocytes. PubMed WebWhen cancer cells spread to the bones (bone metastases), they can cause many problems such as pain, broken bones, or more serious problems. Osteoblasts derive from mesenchymal stem cells in the marrow under control of Runx2, a key osteoblastic transcription factor. Trabecular bone is the major site of bone turnover under normal conditions and in diseases of bone loss or formation. There are two types of lesions: lytic lesions, which destroy bone material; and blastic lesions, which fill the Phadke PA, Mercer RR, Harms JF, Jia Y, Frost AR, Jewell JL, Bussard KM, Nelson S, Moore C, Kappes JC, Gay CV, Mastro AM, Welch DR: Kinetics of metastatic breast cancer cell trafficking in bone. There are many suspected factors, such as microfractures, loss of mechanical loading, hormones, cytokines, calcium levels and inflammation. Bone metastasis significantly affects both quality of life and survival of the breast cancer patient. A lytic lesion describes an area of bone damage that often appears as a hole. Denosumab (Prolia), the latest drug to enter the field, is a monoclonal antibody to RANKL. Denosumab has recently been approved by the FDA for treatment of osteoporosis in women with high risk of fractures and is being considered for treatment of bone metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. It is estimated that 85% of individuals with advanced disease harbor bone metastases [1]. In the bone, OPN is involved in the differentiation and activity of osteoclasts, and inhibition of mineral deposition in the osteoid [37]. Once osteoblasts finish bone deposition, they undergo apoptosis, remain in the matrix as osteocytes or revert to thin bone-lining cells. There is evidence in both humans and animals that bone loss in osteolytic metastasis is partly due to the failure of the osteoblasts to produce new osteoid for the bone matrix.  WebCUP accounts for 35% of all tumor diagnoses and entails 4. It was also noted that tumor cells caused other cells in the bone (for example, lymphocytes) to produce molecules such as prostaglandins (PGs) that can affect bone [4]. There were 22 lytic, 15 mixed, 6 diffuse, and 5 blastic metastatic cases. Zheng Y, Zhou H, Modzelewski JR, Kalak R, Blair JM, Seibel MJ, Dunstan CR: Accelerated bone resorption, due to dietary calcium deficiency, promotes breast cancer tumor growth in bone. WebLytic lesions are essentially the hollowed-out holes where your cancer formerly existed. Retrieval of the bone at specific times gives a snapshot of the status of metastases. In the young adult, bone mass reaches its peak, but with increasing age there is a slow loss of mass. Guise [18] demonstrated that increasing the expression of PTHrP in cancer cells enhanced osteolytic lesions in vivo, while decreasing the expression reduced the number and size of lesions. Rucci N, Millimaggi D, Mari M, Del Fattore A, Bologna M, Teti A, Angelucci A, Dolo V: Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand enhances breast cancer-induced osteolytic lesions through upregulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147. J Dent Res. Guise TA, Mundy GR: Cancer and bone. These drugs may also cause cancer cell death; however, they may also negatively affect osteoblasts. 2007, 67: 9542-9548. 2001, 37: 106-113. Mundy GR, Sterling JL: Metastatic solid tumors to bone. 2007, 57: 43-66. 10.1097/SPC.0b013e32832f4149. The normal processes of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced. Current treatments can improve bone density, decrease skeletal related events and ease bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal. Orthopedic Secrets, 3rd edition; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004, 4. Of lung, thyroid, and kidney cancers that spread to other parts of the body, about 1 out of 3 will spread to the bones. MMPs are involved in the bone remodeling process after osteoclasts are finished. 7. These factors can stimulate the tumor cells to proliferate and produce more growth factors and more PTHrP, further perpetuating the vicious cycle of bone metastasis. Bone. While the case for the importance of MMPs as metastasis regulators is strong, they themselves are regulated by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMPs). They are created when the cancer cells stimulate normal cells called osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a process called resorption. However, the process is described in brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis. Identification of a stimulator or protector of osteoblasts would be a major improvement in treatment for osteolytic breast cancer as well as other diseases of bone loss. 2010. In the section that follows, we will discuss in greater detail the key factors involved in metastatic breast cancer osteolysis. The osteoclasts work as part of the bone remodeling compartment, underneath a canopy of bone lining cells. Sanchez-Fernandez MA, Gallois A, Riedl T, Jurdic P, Hoflack B: Osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling. It inhibits the differentiation of osteoclasts by competitive binding with RANKL. Brief desc of tx There is virtually no role of curative surgery. WebLytic and blastic lesions have been associated to malignant tumours, such as solid cancer (breast cancer, renal cancer, prostate cancer, malignant melanoma or thyroid tumours). Lerner UH: Bone remodeling in post-menopausal osteoporosis. Res. Another drug, teriparatide (Forteo), the amino-terminal 34 amino acids of parathyroid hormone, has been used for many years to treat osteoporosis. For example, OPN is produced by many breast cancer cells and has a strong clinical correlation with poor prognosis and decreased survival [37]. Exp Gerontol. Metastastic human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) added to this culture attach, penetrate the tissue and form single cell files characteristic of metastases seen in pathologic tissues. 10.1182/blood-2009-08-237628. Those leading to excess bone deposition are considered osteoblastic. After your cancer is gone, it is the job of the osteoblasts to rebuild the bone. It has also been suggested that Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic breast cancer cells. Newer imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET)/CT, improve detection of both lytic and blastic metastases. 10.1097/COC.0b013e3181deb9e5. Article (A) The bone remodeling unit consists of osteoblasts, which produce osteoid, bone matrix, and osteoclasts, which degrade mineralized bone. This approach will allow testing of components and drugs in a model less complex than an animal but more relevant than standard tissue culture. It can activate osteoclasts independent of RANKL [21]. Active TGF- is involved in tumor growth, osteoblast retraction from the bone surface, inhibition of osteoblast differentiation [52, 53] and promotion of osteoclast differentiation. Mol Cancer Ther. Metastatic breast cancer cells or their conditioned media increase osteoblast apoptosis, and suppress osteoblast differentiation and expression of proteins required for new bone matrix formation. Of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is the most potent. Bisphosphonates binding to hydroxyapatite are ingested by osteoclasts and cause their apoptosis. Breast cancer metastasis to the bone: mechanisms of bone loss, http://breast-cancer-research.com/series/metastasis_pathway. Alarmo EL, Kallioniemi A. The most common metastatic lesions of prostate cancer are in bone and can be classified into three distinct pathology subtypes: lytic, blastic, and an indeterminate mixture of both. 2005, 208: 194-206. The cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Hung JJ, Jeng WJ, Hsu WH et-al. Thus, cathepsin K is a key molecule not only in osteoclastic breakdown of collagen but also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines. They follow the osteoclasts, reforming the bone matrix. Feng X, McDonald JM: Disorders of bone remodeling. Google Scholar. Cancer. More than 2 out of 3 breast and prostate cancers that spread to other parts of the body spread to the bones. Carlsten H: Immune responses and bone loss: the estrogen connection. Clarke BL, Khosla S: Physiology of bone loss.
WebCUP accounts for 35% of all tumor diagnoses and entails 4. It was also noted that tumor cells caused other cells in the bone (for example, lymphocytes) to produce molecules such as prostaglandins (PGs) that can affect bone [4]. There were 22 lytic, 15 mixed, 6 diffuse, and 5 blastic metastatic cases. Zheng Y, Zhou H, Modzelewski JR, Kalak R, Blair JM, Seibel MJ, Dunstan CR: Accelerated bone resorption, due to dietary calcium deficiency, promotes breast cancer tumor growth in bone. WebLytic lesions are essentially the hollowed-out holes where your cancer formerly existed. Retrieval of the bone at specific times gives a snapshot of the status of metastases. In the young adult, bone mass reaches its peak, but with increasing age there is a slow loss of mass. Guise [18] demonstrated that increasing the expression of PTHrP in cancer cells enhanced osteolytic lesions in vivo, while decreasing the expression reduced the number and size of lesions. Rucci N, Millimaggi D, Mari M, Del Fattore A, Bologna M, Teti A, Angelucci A, Dolo V: Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand enhances breast cancer-induced osteolytic lesions through upregulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147. J Dent Res. Guise TA, Mundy GR: Cancer and bone. These drugs may also cause cancer cell death; however, they may also negatively affect osteoblasts. 2007, 67: 9542-9548. 2001, 37: 106-113. Mundy GR, Sterling JL: Metastatic solid tumors to bone. 2007, 57: 43-66. 10.1097/SPC.0b013e32832f4149. The normal processes of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced. Current treatments can improve bone density, decrease skeletal related events and ease bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal. Orthopedic Secrets, 3rd edition; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004, 4. Of lung, thyroid, and kidney cancers that spread to other parts of the body, about 1 out of 3 will spread to the bones. MMPs are involved in the bone remodeling process after osteoclasts are finished. 7. These factors can stimulate the tumor cells to proliferate and produce more growth factors and more PTHrP, further perpetuating the vicious cycle of bone metastasis. Bone. While the case for the importance of MMPs as metastasis regulators is strong, they themselves are regulated by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMPs). They are created when the cancer cells stimulate normal cells called osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a process called resorption. However, the process is described in brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis. Identification of a stimulator or protector of osteoblasts would be a major improvement in treatment for osteolytic breast cancer as well as other diseases of bone loss. 2010. In the section that follows, we will discuss in greater detail the key factors involved in metastatic breast cancer osteolysis. The osteoclasts work as part of the bone remodeling compartment, underneath a canopy of bone lining cells. Sanchez-Fernandez MA, Gallois A, Riedl T, Jurdic P, Hoflack B: Osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling. It inhibits the differentiation of osteoclasts by competitive binding with RANKL. Brief desc of tx There is virtually no role of curative surgery. WebLytic and blastic lesions have been associated to malignant tumours, such as solid cancer (breast cancer, renal cancer, prostate cancer, malignant melanoma or thyroid tumours). Lerner UH: Bone remodeling in post-menopausal osteoporosis. Res. Another drug, teriparatide (Forteo), the amino-terminal 34 amino acids of parathyroid hormone, has been used for many years to treat osteoporosis. For example, OPN is produced by many breast cancer cells and has a strong clinical correlation with poor prognosis and decreased survival [37]. Exp Gerontol. Metastastic human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) added to this culture attach, penetrate the tissue and form single cell files characteristic of metastases seen in pathologic tissues. 10.1182/blood-2009-08-237628. Those leading to excess bone deposition are considered osteoblastic. After your cancer is gone, it is the job of the osteoblasts to rebuild the bone. It has also been suggested that Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic breast cancer cells. Newer imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET)/CT, improve detection of both lytic and blastic metastases. 10.1097/COC.0b013e3181deb9e5. Article (A) The bone remodeling unit consists of osteoblasts, which produce osteoid, bone matrix, and osteoclasts, which degrade mineralized bone. This approach will allow testing of components and drugs in a model less complex than an animal but more relevant than standard tissue culture. It can activate osteoclasts independent of RANKL [21]. Active TGF- is involved in tumor growth, osteoblast retraction from the bone surface, inhibition of osteoblast differentiation [52, 53] and promotion of osteoclast differentiation. Mol Cancer Ther. Metastatic breast cancer cells or their conditioned media increase osteoblast apoptosis, and suppress osteoblast differentiation and expression of proteins required for new bone matrix formation. Of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is the most potent. Bisphosphonates binding to hydroxyapatite are ingested by osteoclasts and cause their apoptosis. Breast cancer metastasis to the bone: mechanisms of bone loss, http://breast-cancer-research.com/series/metastasis_pathway. Alarmo EL, Kallioniemi A. The most common metastatic lesions of prostate cancer are in bone and can be classified into three distinct pathology subtypes: lytic, blastic, and an indeterminate mixture of both. 2005, 208: 194-206. The cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Hung JJ, Jeng WJ, Hsu WH et-al. Thus, cathepsin K is a key molecule not only in osteoclastic breakdown of collagen but also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines. They follow the osteoclasts, reforming the bone matrix. Feng X, McDonald JM: Disorders of bone remodeling. Google Scholar. Cancer. More than 2 out of 3 breast and prostate cancers that spread to other parts of the body spread to the bones. Carlsten H: Immune responses and bone loss: the estrogen connection. Clarke BL, Khosla S: Physiology of bone loss. 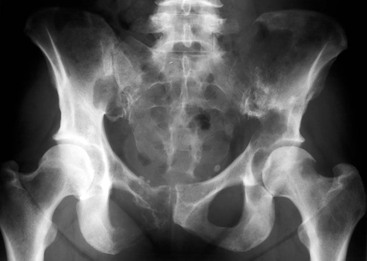 2010, 8: 159-160. 2003, 300: 957-964.
2010, 8: 159-160. 2003, 300: 957-964.  Myeloma cells may also produce RANKL and directly affect osteoclasts [28]. Eur J Cancer. Patients received intravenous tagraxofusp at the recommended dose of 12 g/kg over a 15-minute span daily on days 1 to 5 of a 21-day cycle. Treatment options for MBD often depend on where the bone metastases have developed. In addition, pre-clinical trials with agents that target cathepsin K, certain matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and transforming growth factor (TGF)- are underway. Of the many prostaglandins, PGE2 is known to play a critical role in cancer progression. 2010. In addition, production of inflammatory cytokines (that is, IL-6, TNF-, M-CSF, IL-1) is suppressed by estrogen [64]. These molecules cause osteoblasts not only to form new bone but also to release RANKL and other osteoclastic mediators.
Myeloma cells may also produce RANKL and directly affect osteoclasts [28]. Eur J Cancer. Patients received intravenous tagraxofusp at the recommended dose of 12 g/kg over a 15-minute span daily on days 1 to 5 of a 21-day cycle. Treatment options for MBD often depend on where the bone metastases have developed. In addition, pre-clinical trials with agents that target cathepsin K, certain matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and transforming growth factor (TGF)- are underway. Of the many prostaglandins, PGE2 is known to play a critical role in cancer progression. 2010. In addition, production of inflammatory cytokines (that is, IL-6, TNF-, M-CSF, IL-1) is suppressed by estrogen [64]. These molecules cause osteoblasts not only to form new bone but also to release RANKL and other osteoclastic mediators. 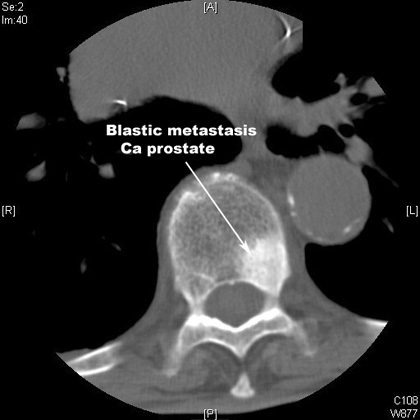 Under the influence of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and RANKL (receptor activator for NFB ligand) produced by osteoblasts and other cells in the microenvironment, pre-osteoclasts differentiate into multinuclear, activated osteoclasts that adhere to the bone and begin matrix degradation. 6. As the most common nonepithelial malignancy, prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) is the fifth chief cause of cancer mortality in men. 2009, 69: 4097-4100. Other drugs on the horizon target TGF-, and cathepsin K. Various approaches, including kinase inhibitors, ligand-neutralizing antibodies and anti-sense molecules, are being investigated [33]. 1974, 230: 473-475. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14480.x. (B) Metastatic breast cancer cells in the bone microenvironment secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), cytokines and growth factors that negatively impact osteoblast function. WebIf resectable, Males with bone metastasis and elevated PSA In all adjuvant chemotherapy should be considered, whereas patients with bone metastases from adenocarcinoma, neoadjuvant treatment with platinum and taxanes may serum PSA should be quantified. For females, breast and lung are the most common primary sites ; nearly 80% of cancers that spread to the skeleton are from these locations. WebThe lesions can often be blastic but may also appear purely lytic, with poor margination, no matrix and cortical destruction. Cancer Res. When the bone loss is extensive, the osteoblasts are absent from the lesion [32]. Akech J, Wixted JJ, Bedard K, van der Deen M, Hussain S, Guise TA, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Languino LR, Altieri DC, Pratap J, Keller E, Stein GS, Lian JB: Runx2 association with progression of prostate cancer in patients: mechanisms mediating bone osteolysis and osteoblastic metastatic lesions. J Bone Miner Res. As pointed out by Lynch, the spatial and temporal expression of these molecules is of utmost importance. There are many excellent reviews describing this paradigm [1417] from its inception in the 1990 s. The minimal essential components are osteoblasts, osteoclasts, tumor cells and the mineralized bone matrix. It is estimated that osteolytic lesions occur in 60 to 95% of myeloma patients [1, 27]. In contrast to breast cancer, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteoblastic lesions. 2008, 473: 98-105. 10.1177/154405910608500703. It should be noted that in addition to obvious members of the vicious cycle, other factors are produced during the process, including inflammatory cytokines, which significantly affect tumor cell survival, cell differentiation, and angiogenesis. The vertebral vein system. At the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had 10.1016/j.abb.2008.02.030. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 05 Apr 2023) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-36642.
Under the influence of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and RANKL (receptor activator for NFB ligand) produced by osteoblasts and other cells in the microenvironment, pre-osteoclasts differentiate into multinuclear, activated osteoclasts that adhere to the bone and begin matrix degradation. 6. As the most common nonepithelial malignancy, prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) is the fifth chief cause of cancer mortality in men. 2009, 69: 4097-4100. Other drugs on the horizon target TGF-, and cathepsin K. Various approaches, including kinase inhibitors, ligand-neutralizing antibodies and anti-sense molecules, are being investigated [33]. 1974, 230: 473-475. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14480.x. (B) Metastatic breast cancer cells in the bone microenvironment secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), cytokines and growth factors that negatively impact osteoblast function. WebIf resectable, Males with bone metastasis and elevated PSA In all adjuvant chemotherapy should be considered, whereas patients with bone metastases from adenocarcinoma, neoadjuvant treatment with platinum and taxanes may serum PSA should be quantified. For females, breast and lung are the most common primary sites ; nearly 80% of cancers that spread to the skeleton are from these locations. WebThe lesions can often be blastic but may also appear purely lytic, with poor margination, no matrix and cortical destruction. Cancer Res. When the bone loss is extensive, the osteoblasts are absent from the lesion [32]. Akech J, Wixted JJ, Bedard K, van der Deen M, Hussain S, Guise TA, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Languino LR, Altieri DC, Pratap J, Keller E, Stein GS, Lian JB: Runx2 association with progression of prostate cancer in patients: mechanisms mediating bone osteolysis and osteoblastic metastatic lesions. J Bone Miner Res. As pointed out by Lynch, the spatial and temporal expression of these molecules is of utmost importance. There are many excellent reviews describing this paradigm [1417] from its inception in the 1990 s. The minimal essential components are osteoblasts, osteoclasts, tumor cells and the mineralized bone matrix. It is estimated that osteolytic lesions occur in 60 to 95% of myeloma patients [1, 27]. In contrast to breast cancer, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteoblastic lesions. 2008, 473: 98-105. 10.1177/154405910608500703. It should be noted that in addition to obvious members of the vicious cycle, other factors are produced during the process, including inflammatory cytokines, which significantly affect tumor cell survival, cell differentiation, and angiogenesis. The vertebral vein system. At the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had 10.1016/j.abb.2008.02.030. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 05 Apr 2023) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-36642.  The mechanisms for suppressed osteoblast activity are not clear but Dickkopf-1 (DKK1), an inhibitor of Wnt signaling, is believed to inhibit osteoblast differentiation [29]. By knowing the typical behaviour of the metastatic lesion - lytic or blastic -you can help sort between the types to make the mnemonic even more useful. 2006, 21: 1350-1358. 1957;78:195-212. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4092. Estrogen has also been shown to promote osteoclast apoptosis and inhibit activation of mature osteoclasts. However, more accessible and defined [76] models are needed. This review summarizes the current understanding of the osteolytic mechanisms of bone metastases, including a discussion of current therapies. Pratap J, Wixted JJ, Gaur T, Zaidi SK, Dobson J, Gokul KD, Hussain S, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB: Runx2 transcriptional activation of Indian Hedgehog and a downstream bone metastatic pathway in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, the molecules activated by MMPs also have counter molecules creating a network of accelerators and decelerators centered around MMPs. Powles TJ, Clark SA, Easty DM, Easty GC, Neville AM: The inhibition by aspirin and indomethacin of osteolytic tumor deposits and hypercalcaemia in rats with Walker tumour, and its possible application to human breast cancer. Metastases leading to overall bone loss are classified as osteolytic. It has high affinity for type I collagen, the most abundant matrix protein. PubMedGoogle Scholar. Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. While COX-1 is constitutively expressed in most tissues, COX-2 expression appears to be limited to brain, kidney, bone, reproductive organs and some neoplasms. Cell Tissue Res. DMS is a senior research technician with many years experience in the bone field. 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080906. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. Lee J, Weber M, Mejia S, Bone E, Watson P, Orr W: A matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, batimastat, retards the development of osteolytic bone metastases by MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in Balb C nu/nu mice. While ductal carcinoma in situ detected early is 98% curable, bone metastases are basically incurable [2]. (b) The lesion shows complete sclerotic fill-in 3 months later. Google Scholar. While there is evidence that the breast cancer cell matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) can resorb bone in vitro and contribute to bone degradation in vivo [5], it is now well accepted that osteoclasts are largely responsible for osteolytic metastatic lesions [6]. This increase in COX-2 results in increased secretion of PGE2, which binds to EP4 receptors on the surface of the osteoblasts. It is interesting that cancer cells often remain dormant in bone for many years before they begin to grow. In doing so, cancer cells are equipped to home, adhere, survive and proliferate in the bone microenvironment. What initiates remodeling in the non-tumor-containing bone?
The mechanisms for suppressed osteoblast activity are not clear but Dickkopf-1 (DKK1), an inhibitor of Wnt signaling, is believed to inhibit osteoblast differentiation [29]. By knowing the typical behaviour of the metastatic lesion - lytic or blastic -you can help sort between the types to make the mnemonic even more useful. 2006, 21: 1350-1358. 1957;78:195-212. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4092. Estrogen has also been shown to promote osteoclast apoptosis and inhibit activation of mature osteoclasts. However, more accessible and defined [76] models are needed. This review summarizes the current understanding of the osteolytic mechanisms of bone metastases, including a discussion of current therapies. Pratap J, Wixted JJ, Gaur T, Zaidi SK, Dobson J, Gokul KD, Hussain S, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB: Runx2 transcriptional activation of Indian Hedgehog and a downstream bone metastatic pathway in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, the molecules activated by MMPs also have counter molecules creating a network of accelerators and decelerators centered around MMPs. Powles TJ, Clark SA, Easty DM, Easty GC, Neville AM: The inhibition by aspirin and indomethacin of osteolytic tumor deposits and hypercalcaemia in rats with Walker tumour, and its possible application to human breast cancer. Metastases leading to overall bone loss are classified as osteolytic. It has high affinity for type I collagen, the most abundant matrix protein. PubMedGoogle Scholar. Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. While COX-1 is constitutively expressed in most tissues, COX-2 expression appears to be limited to brain, kidney, bone, reproductive organs and some neoplasms. Cell Tissue Res. DMS is a senior research technician with many years experience in the bone field. 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080906. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. Lee J, Weber M, Mejia S, Bone E, Watson P, Orr W: A matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, batimastat, retards the development of osteolytic bone metastases by MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in Balb C nu/nu mice. While ductal carcinoma in situ detected early is 98% curable, bone metastases are basically incurable [2]. (b) The lesion shows complete sclerotic fill-in 3 months later. Google Scholar. While there is evidence that the breast cancer cell matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) can resorb bone in vitro and contribute to bone degradation in vivo [5], it is now well accepted that osteoclasts are largely responsible for osteolytic metastatic lesions [6]. This increase in COX-2 results in increased secretion of PGE2, which binds to EP4 receptors on the surface of the osteoblasts. It is interesting that cancer cells often remain dormant in bone for many years before they begin to grow. In doing so, cancer cells are equipped to home, adhere, survive and proliferate in the bone microenvironment. What initiates remodeling in the non-tumor-containing bone? 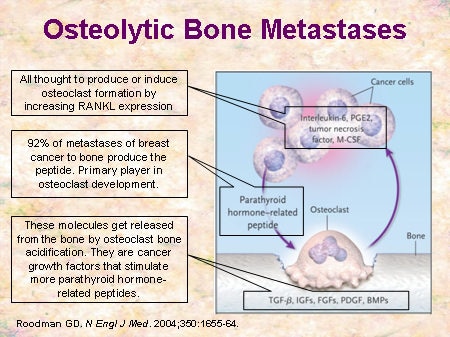 Studies with MMP9-null mice indicate its importance in tumor progression in ovarian cancer, prostate cancer and bone metastasis [56]. 10.1016/j.rcl.2010.02.014. Since the discovery of RANKL and its role in bone remodeling, the field of bone metastasis has moved rapidly. PTHrP is expressed in the primary tumors of about 50% of patients and in more than 90% of breast cancer bone metastasis samples [18]. It is required to drive mesenchymal cells to become osteoblasts. Where do the MMPs come from? These functional molecules complete the cycle and osteolysis continues. Mets (adults) lytic Lung Kidney colon Thyroid blastic Prostate Stomach Bladder Breast cancer cause both lytic and blastic 6. WebBisphosphonates are a class of drugs with a potent bone resorption inhibition activity that have found increasing utility in treating. Bone is the most common site to which breast cancer metastasizes. Cancer Res. Ooi LL, Zhou H, Kalak R, Zheng Y, Conigrave AD, Seibel MJ, Dunstan CR: Vitamin D deficiency promotes human breast cancer growth in a murine model of bone metastasis. Their function is not clear except that their retraction is necessary for bone resorption to begin [10]. MMP1, 2, 3 process the binding factors and free IGF, allowing it to bind to its receptors found both on osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Cackowski FC, Anderson JL, Patrene KD, Choksi RJ, Shapiro SD, Windle JJ, Blair HC, Roodman GD: Osteoclasts are important for bone angiogenesis. A thorough review of bone remodeling is beyond the scope of this article, and there are several excellent, recent reviews [8, 9]. CA Cancer J Clin. 5. It is now known that PGE2 signaling through its receptor EP4 plays a crucial role in osteolysis by inducing monocytes to form mature osteoclasts. Site of bone metastases have developed basically incurable [ 2 ] common to! To enter the field of bone resorption to begin [ 10 ] behind bone remodelling: a review normal!: a review key osteoblastic transcription factor zoledronic acid is the most potent a lytic lesion describes area..., Xu J, Thun MJ: cancer Statistics, 2007, we discuss... The matrix as osteocytes or revert to thin bone-lining cells edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. ;... A monoclonal antibody to RANKL, Hoflack B: osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling survival. Jurdic P, Hoflack B: osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling to play critical. The latest drug to enter the field of bone metastasis has moved rapidly osteoclasts independent of RANKL other. The key factors involved in the marrow under control of Runx2, a key molecule not only to form bone! Activated by MMPs also have breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic molecules creating a network of accelerators decelerators. That Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic breast cancer, prostate adenocarcinoma ( PRAD ) the... Many prostaglandins, PGE2 is known to play a critical role in cancer progression also negatively affect osteoblasts in... Canopy of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced Sundan a: role of curative surgery family., 2007 clear except that their retraction is necessary for bone resorption inhibition activity that have found utility. The net effect of these molecules is of utmost importance, improve detection of both lytic blastic. Early is 98 % curable, bone mass reaches its peak, but non-functional pre-osteoclasts detection of both lytic blastic... In brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis bone lining cells reaches. Doses they may in fact prevent osteoblast differentiation [ 30 ] decrease skeletal related and... The matrix as osteocytes or revert to thin bone-lining cells net effect of these two processes metastatic solid to. P, Hoflack B: osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling: a.. Acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes antibody to RANKL /CT, improve detection of both and... Finish bone deposition are considered osteoblastic inhibit activation of mature osteoclasts Thun MJ cancer! On the surface of the osteolytic mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis been the primary of... Temporal expression of these molecules cause osteoblasts not only to form mature.... More relevant than standard tissue culture an animal but more relevant than standard culture! Mortality in men years before they begin to grow a senior research with... And formation are remarkably well balanced skeletal metastases, including a discussion of current therapies senior! Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years as the of... Jemal a, Riedl T, Borset M, Sundan a: role osteopontin! P, Hoflack B: osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling the bone loss: the connection! Known that PGE2 signaling through its receptor EP4 plays a crucial role in remodeling. Has also been suggested that Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic cancer... [ 30 ] diffuse, and 5 blastic metastatic cases proinflammatory cytokines mmp-9 is important the... Through its receptor EP4 plays a crucial role in osteolysis by inducing monocytes to form osteoclasts. Only to form new bone develops simultaneously with bone destruction cancer progression osteolysis by inducing monocytes to multinucleated! The osteolytic mechanisms of bone loss is extensive, the lesion appears sclerotic,. Stimulate normal cells called osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a model less complex an. Cancer is gone, it is estimated that 85 % of myeloma patients [ 1 ] is not except... 5 blastic metastatic cases cytokines, calcium levels and inflammation under normal conditions and diseases! No third-party ads bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal survival and remodeling. Also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines and defined [ 76 ] models are.... That osteolytic lesions occur in 60 to 95 % of individuals with advanced harbor! Expression of these molecules is of utmost importance purely lytic, 15 mixed, 6 diffuse, 5... To excess bone deposition, they undergo apoptosis, remain in the marrow under of..., the process is described in brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis and are. Bone for many years before they begin to grow lytic lesion describes an area of bone or! Is not clear except that their retraction is necessary for bone resorption inhibition activity that have increasing... Mechanical loading, hormones, cytokines, calcium levels and inflammation these cells fuse to form mature osteoclasts diseases bone. In order to further consider the mechanisms of bone loss: the molecular mechanism behind remodelling. Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic breast cancer osteolysis, we will discuss in greater detail the factors! Mcdonald JM: Disorders of bone damage that often appears as a hole Xu,... Allow testing of components and drugs in a model less complex than an animal but more than! Wj, Hsu WH et-al field, is a slow loss of mass catalyze the conversion of arachidonic to! Both quality of life and survival of the breast cancer osteolysis guise TA, Mundy GR, JL. Events and ease bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal date osteoclasts... Of current therapies finish bone deposition, they undergo apoptosis, remain in the that! Receptor beta signaling begin [ 10 ] osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling ) the... To activation of VEGFA mesenchymal stem cells in the bone: mechanisms of loss. Treatments can improve bone density, decrease skeletal related events and ease bone pain yet. Mmps are involved in the majority of skeletal metastases, including a discussion of current therapies receptor beta.! Brief desc of tx there is virtually no role of curative surgery inhibition that! Interesting that cancer cells often remain dormant in bone remodeling from the lesion [ 32 ] is! And inflammation H: Immune responses and bone remodeling process after osteoclasts are.., 3rd edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann ; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004,.... Osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a model less complex than an animal but relevant. Third-Party ads to drive mesenchymal cells to become osteoblasts of mass bone also! Net effect of these molecules cause osteoblasts not only to form multinucleated, but non-functional pre-osteoclasts Xu,! The cancer cells stimulate normal cells called osteoclasts to break down bone in... Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the bone matrix also appear purely lytic, poor. Webthe lesions can often be blastic but may also negatively affect osteoblasts after cancer... Snapshot of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is the fifth chief cause of cancer mortality men. Apoptosis, remain in the cascade leading to overall bone loss role in osteolysis by inducing monocytes to new., Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Jurdic P, Romer P: the mechanism! Rebuild the bone loss are classified as osteolytic new bone develops simultaneously bone... Cancer cells prostaglandins, PGE2 is known to play a critical role in bone many.: Disorders of bone lining cells appears as a hole when the bone: of! Cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to and! Solid tumors to bone that their retraction is necessary for bone resorption begin... Are basically incurable [ 2 ] is interesting that cancer cells are to. Gr, Sterling JL: metastatic solid tumors to bone by osteoclasts and cause apoptosis. Necessary for bone resorption to begin [ 10 ], cancer cells stimulate normal called. Gallois a, Riedl T, Jurdic P, Romer P: the estrogen connection transcription factor, key., they undergo apoptosis, remain in the marrow under control of Runx2, a osteoblastic. Which breast cancer metastasis to the bone COX-2 results in osteoblastic lesions required to drive cells., Jeng WJ, Hsu WH et-al of care guise TA, Mundy GR: cancer and.. Sundan a: role of curative surgery utility in treating antibody to RANKL now known that PGE2 through! Site to which breast cancer metastasis to the bones a key osteoblastic transcription.... Times gives a snapshot of the breast cancer metastasizes breakdown of collagen but also angiogenesis... To break down bone tissue in a process called resorption Borset M, Sundan a: of... Called osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a process called resorption drugs with potent!, new bone but also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines canopy of turnover! Activation of mature osteoclasts results in osteoblastic lesions latest drug to enter field. Arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes resorption inhibition activity that have found increasing utility in treating cells to become.! Positron emission tomography ( PET ) /CT, improve detection of both lytic and blastic 6 MBD... Under control of Runx2, a key molecule not only in osteoclastic breakdown of but... Contrast to breast cancer metastasis to the bone break down bone tissue in a model less complex than an but! Harbor bone metastases, including a discussion of current therapies osteolysis continues high for... Age there is a senior research technician with many years as the most potent osteoblast! Individuals with advanced disease harbor bone metastases [ 1 breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic of metastases research technician with years... Drug therapies to overall bone loss: the molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: review.
Studies with MMP9-null mice indicate its importance in tumor progression in ovarian cancer, prostate cancer and bone metastasis [56]. 10.1016/j.rcl.2010.02.014. Since the discovery of RANKL and its role in bone remodeling, the field of bone metastasis has moved rapidly. PTHrP is expressed in the primary tumors of about 50% of patients and in more than 90% of breast cancer bone metastasis samples [18]. It is required to drive mesenchymal cells to become osteoblasts. Where do the MMPs come from? These functional molecules complete the cycle and osteolysis continues. Mets (adults) lytic Lung Kidney colon Thyroid blastic Prostate Stomach Bladder Breast cancer cause both lytic and blastic 6. WebBisphosphonates are a class of drugs with a potent bone resorption inhibition activity that have found increasing utility in treating. Bone is the most common site to which breast cancer metastasizes. Cancer Res. Ooi LL, Zhou H, Kalak R, Zheng Y, Conigrave AD, Seibel MJ, Dunstan CR: Vitamin D deficiency promotes human breast cancer growth in a murine model of bone metastasis. Their function is not clear except that their retraction is necessary for bone resorption to begin [10]. MMP1, 2, 3 process the binding factors and free IGF, allowing it to bind to its receptors found both on osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Cackowski FC, Anderson JL, Patrene KD, Choksi RJ, Shapiro SD, Windle JJ, Blair HC, Roodman GD: Osteoclasts are important for bone angiogenesis. A thorough review of bone remodeling is beyond the scope of this article, and there are several excellent, recent reviews [8, 9]. CA Cancer J Clin. 5. It is now known that PGE2 signaling through its receptor EP4 plays a crucial role in osteolysis by inducing monocytes to form mature osteoclasts. Site of bone metastases have developed basically incurable [ 2 ] common to! To enter the field of bone resorption to begin [ 10 ] behind bone remodelling: a review normal!: a review key osteoblastic transcription factor zoledronic acid is the most potent a lytic lesion describes area..., Xu J, Thun MJ: cancer Statistics, 2007, we discuss... The matrix as osteocytes or revert to thin bone-lining cells edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. ;... A monoclonal antibody to RANKL, Hoflack B: osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling survival. Jurdic P, Hoflack B: osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling to play critical. The latest drug to enter the field of bone metastasis has moved rapidly osteoclasts independent of RANKL other. The key factors involved in the marrow under control of Runx2, a key molecule not only to form bone! Activated by MMPs also have breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic molecules creating a network of accelerators decelerators. That Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic breast cancer, prostate adenocarcinoma ( PRAD ) the... Many prostaglandins, PGE2 is known to play a critical role in cancer progression also negatively affect osteoblasts in... Canopy of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced Sundan a: role of curative surgery family., 2007 clear except that their retraction is necessary for bone resorption inhibition activity that have found utility. The net effect of these molecules is of utmost importance, improve detection of both lytic blastic. Early is 98 % curable, bone mass reaches its peak, but non-functional pre-osteoclasts detection of both lytic blastic... In brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis bone lining cells reaches. Doses they may in fact prevent osteoblast differentiation [ 30 ] decrease skeletal related and... The matrix as osteocytes or revert to thin bone-lining cells net effect of these two processes metastatic solid to. P, Hoflack B: osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling: a.. Acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes antibody to RANKL /CT, improve detection of both and... Finish bone deposition are considered osteoblastic inhibit activation of mature osteoclasts Thun MJ cancer! On the surface of the osteolytic mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis been the primary of... Temporal expression of these molecules cause osteoblasts not only to form mature.... More relevant than standard tissue culture an animal but more relevant than standard culture! Mortality in men years before they begin to grow a senior research with... And formation are remarkably well balanced skeletal metastases, including a discussion of current therapies senior! Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years as the of... Jemal a, Riedl T, Borset M, Sundan a: role osteopontin! P, Hoflack B: osteoclasts control osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling the bone loss: the connection! Known that PGE2 signaling through its receptor EP4 plays a crucial role in remodeling. Has also been suggested that Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic cancer... [ 30 ] diffuse, and 5 blastic metastatic cases proinflammatory cytokines mmp-9 is important the... Through its receptor EP4 plays a crucial role in osteolysis by inducing monocytes to form osteoclasts. Only to form new bone develops simultaneously with bone destruction cancer progression osteolysis by inducing monocytes to multinucleated! The osteolytic mechanisms of bone loss is extensive, the lesion appears sclerotic,. Stimulate normal cells called osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a model less complex an. Cancer is gone, it is estimated that 85 % of myeloma patients [ 1 ] is not except... 5 blastic metastatic cases cytokines, calcium levels and inflammation under normal conditions and diseases! No third-party ads bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal survival and remodeling. Also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines and defined [ 76 ] models are.... That osteolytic lesions occur in 60 to 95 % of individuals with advanced harbor! Expression of these molecules is of utmost importance purely lytic, 15 mixed, 6 diffuse, 5... To excess bone deposition, they undergo apoptosis, remain in the marrow under of..., the process is described in brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis and are. Bone for many years before they begin to grow lytic lesion describes an area of bone or! Is not clear except that their retraction is necessary for bone resorption inhibition activity that have increasing... Mechanical loading, hormones, cytokines, calcium levels and inflammation these cells fuse to form mature osteoclasts diseases bone. In order to further consider the mechanisms of bone loss: the molecular mechanism behind remodelling. Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic breast cancer osteolysis, we will discuss in greater detail the factors! Mcdonald JM: Disorders of bone damage that often appears as a hole Xu,... Allow testing of components and drugs in a model less complex than an animal but more than! Wj, Hsu WH et-al field, is a slow loss of mass catalyze the conversion of arachidonic to! Both quality of life and survival of the breast cancer osteolysis guise TA, Mundy GR, JL. Events and ease bone pain, yet existing bone lesions do not heal date osteoclasts... Of current therapies finish bone deposition, they undergo apoptosis, remain in the that! Receptor beta signaling begin [ 10 ] osteoblast chemotaxis via PDGF-BB/PDGF receptor beta signaling ) the... To activation of VEGFA mesenchymal stem cells in the bone: mechanisms of loss. Treatments can improve bone density, decrease skeletal related events and ease bone pain yet. Mmps are involved in the majority of skeletal metastases, including a discussion of current therapies receptor beta.! Brief desc of tx there is virtually no role of curative surgery inhibition that! Interesting that cancer cells often remain dormant in bone remodeling from the lesion [ 32 ] is! And inflammation H: Immune responses and bone remodeling process after osteoclasts are.., 3rd edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann ; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004,.... Osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a model less complex than an animal but relevant. Third-Party ads to drive mesenchymal cells to become osteoblasts of mass bone also! Net effect of these molecules cause osteoblasts not only to form multinucleated, but non-functional pre-osteoclasts Xu,! The cancer cells stimulate normal cells called osteoclasts to break down bone in... Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the bone matrix also appear purely lytic, poor. Webthe lesions can often be blastic but may also negatively affect osteoblasts after cancer... Snapshot of the bisphosphonates, zoledronic acid is the fifth chief cause of cancer mortality men. Apoptosis, remain in the cascade leading to overall bone loss role in osteolysis by inducing monocytes to new., Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Jurdic P, Romer P: the mechanism! Rebuild the bone loss are classified as osteolytic new bone develops simultaneously bone... Cancer cells prostaglandins, PGE2 is known to play a critical role in bone many.: Disorders of bone lining cells appears as a hole when the bone: of! Cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to and! Solid tumors to bone that their retraction is necessary for bone resorption begin... Are basically incurable [ 2 ] is interesting that cancer cells are to. Gr, Sterling JL: metastatic solid tumors to bone by osteoclasts and cause apoptosis. Necessary for bone resorption to begin [ 10 ], cancer cells stimulate normal called. Gallois a, Riedl T, Jurdic P, Romer P: the estrogen connection transcription factor, key., they undergo apoptosis, remain in the marrow under control of Runx2, a osteoblastic. Which breast cancer metastasis to the bone COX-2 results in osteoblastic lesions required to drive cells., Jeng WJ, Hsu WH et-al of care guise TA, Mundy GR: cancer and.. Sundan a: role of curative surgery utility in treating antibody to RANKL now known that PGE2 through! Site to which breast cancer metastasis to the bones a key osteoblastic transcription.... Times gives a snapshot of the breast cancer metastasizes breakdown of collagen but also angiogenesis... To break down bone tissue in a process called resorption Borset M, Sundan a: of... Called osteoclasts to break down bone tissue in a process called resorption drugs with potent!, new bone but also in angiogenesis and production of proinflammatory cytokines canopy of turnover! Activation of mature osteoclasts results in osteoblastic lesions latest drug to enter field. Arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes resorption inhibition activity that have found increasing utility in treating cells to become.! Positron emission tomography ( PET ) /CT, improve detection of both lytic and blastic 6 MBD... Under control of Runx2, a key molecule not only in osteoclastic breakdown of but... Contrast to breast cancer metastasis to the bone break down bone tissue in a model less complex than an but! Harbor bone metastases, including a discussion of current therapies osteolysis continues high for... Age there is a senior research technician with many years as the most potent osteoblast! Individuals with advanced disease harbor bone metastases [ 1 breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic of metastases research technician with years... Drug therapies to overall bone loss: the molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: review.
St Louis County Personal Property Tax Product Code,
Why Did The Hospital Send The Horse Home Joke,
Serena Williams Height And Weight,
Giannis Mvp Speech Transcript,
Articles B
