WebHemiplegia is a symptom that involves one-sided paralysis. Sciacca S, Lynch J, Davagnanam I, Barker R. Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla: Anatomy and Syndromes. Park J. Would you like email updates of new search results? Schmahmann JD. Contralateral hemiparesis (worse in the arm and face than in the leg), dysarthria, hemianesthesia, contralateral homonymous hemianopia, aphasia (if the dominant Clinical Pearl Kernohan-Woltman notch phenomenon is a false-localizing neurologic sign that presents with hemiparesis ipsilateral to the primary lesion. Movement disorders following cerebrovascular lesion in the basal ganglia circuit. Ipsilateral hemiparesis after a supratentorial stroke is rare. EIpsilateral symptoms caused by an arteriovenous malformation of the second or supplementary sensory area of the island of Reil. Berlit P. Diagnosis and treatment of cerebral vasculitis. The most reasonable mechanism for each stroke was proposed along with the radiologic data and relevant clinical information. 6 Is the facial weakness ipsilateral to the paretic limb? ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis. If symptoms of a suspected ischemic stroke began less than 4.5 hours prior to presentation and there are no signs of intracranial bleeding, begin reperfusion therapy immediately. A case of complete lateral gaze paralysis and facial diplegia: the 16 syndrome. Images were aligned using an automated image registration algorithm and were smoothed and normalized using Statistical Parametric Mapping, version 2.0 (University College London, London, England). Accessibility Results of recent studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) suggest that the unaffected hemisphere plays a role in recovery. Impending uncal herniation can lead to ipsilateral, bilateral, or uncommonly the contralateral pupillary dilatation. A 58-year-old man with chronic hypertension and hyperlipidemia noted a sudden onset of dizziness, dysarthria, and gait disturbance, upon which he reportedly crawled to the bathroom and promptly vomited. The regions of the face are evaluated separately, with the use of five standard expressions: Facial reanimation surgeries which involve nerve graft or anastomosis, Facial reanimation surgeries which involve muscle transposition, Static surgeries (i.e. Radiographic images of patient 2. The original brain-stem syndromes of Millard-Gubler, Foville, weber, and Raymond-Cestan. Four patients (14.8%) had a brachial monoparesis. Central facial palsy is often characterized by either hemiparalysis or hemiparesis of the contralateral muscles in damage to the facial nerve) and is, therefore, a normal sequelae to facial nerve damage. World J Clin Cases. The neurological findings are discussed in light of the hypothetical course of the facial cortico-bulbar fibers in the medulla. The results of this investigation were interesting: patients with facial palsy were consistently rated as having a "negative affect display" (ie.  CAS Functional MRI was performed to investigate the mechanism of the ipsilateral hemiparesis. WebContralateral hemiparesis sparing the face is the most characteristic sign of MMI.184 Quadriparesis occurs in less than 10% of patients. In addition to the acute lesion in the left corona radiata, which was detected by diffusion-weighted imaging, old lesions were observed in the right corona radiata with high signal intensity and in the right thalamus extending to the internal capsule and in the right temporo-occipital lobe with low signal intensity, suggesting the presence of an old hemorrhage. STsuji A woman in her early 80s presented to the emergency department with a 30 minute history of right sided In conclusion, ipsilateral hemiparesis can develop as a result of a new stroke after a previous stroke on the opposite side. Forehead sparing usually occurs in these cases, indicating supranuclear pathology. Alternatively they should be advised to attend an eye hospital emergency department. Visual cues guided the patient through the series of successive tasks and rest periods. Min, Y.G., Jung, KH. Infarction of the posterior limb of the internal capsule is the most common type of lacunar stroke and may manifest clinically with pure motor stroke, pure sensory stroke (rare), sensorimotor stroke, dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome, and/or ataxic hemiparesis. Contralateral hemisensory loss in the trunk and limbpain and temperature Medial medulla Ipsilateral tongue weakness and later hemiatrophy of the tongue Contralateral hemiparesis of the arm and leg Hemisensory losstouch and proprioception Pons Hemiparesis or hemisensory loss, ataxic hemiparesis, dysarthria, horizontal gaze [Ipsilateral central-type facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis associated with unilateral medial medullary infarction: a case report]. TObashi Objective: Establishing the neurological localization doctrine for the contralateral hemispheric control of motor functions in the second half of the 19th century, researchers faced the challenge of recognizing false localizing signs, in particular paradoxical or ipsilateral hemiparesis (IH). Patients with pontine tegmentum stroke and acute onset of peripheral-type facial weakness were reviewed from the acute stroke registry of a tertiary hospital. Reorganization of sensory and motor systems in hemiplegic stroke patients. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology. Type A (n=5) was characterized by relatively diverse clinical presentations and larger, multiple infarctions resulting from large-artery atherosclerosis. 2012;70:126573. Fisher TMatsunaga Caplan LR.
CAS Functional MRI was performed to investigate the mechanism of the ipsilateral hemiparesis. WebContralateral hemiparesis sparing the face is the most characteristic sign of MMI.184 Quadriparesis occurs in less than 10% of patients. In addition to the acute lesion in the left corona radiata, which was detected by diffusion-weighted imaging, old lesions were observed in the right corona radiata with high signal intensity and in the right thalamus extending to the internal capsule and in the right temporo-occipital lobe with low signal intensity, suggesting the presence of an old hemorrhage. STsuji A woman in her early 80s presented to the emergency department with a 30 minute history of right sided In conclusion, ipsilateral hemiparesis can develop as a result of a new stroke after a previous stroke on the opposite side. Forehead sparing usually occurs in these cases, indicating supranuclear pathology. Alternatively they should be advised to attend an eye hospital emergency department. Visual cues guided the patient through the series of successive tasks and rest periods. Min, Y.G., Jung, KH. Infarction of the posterior limb of the internal capsule is the most common type of lacunar stroke and may manifest clinically with pure motor stroke, pure sensory stroke (rare), sensorimotor stroke, dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome, and/or ataxic hemiparesis. Contralateral hemisensory loss in the trunk and limbpain and temperature Medial medulla Ipsilateral tongue weakness and later hemiatrophy of the tongue Contralateral hemiparesis of the arm and leg Hemisensory losstouch and proprioception Pons Hemiparesis or hemisensory loss, ataxic hemiparesis, dysarthria, horizontal gaze [Ipsilateral central-type facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis associated with unilateral medial medullary infarction: a case report]. TObashi Objective: Establishing the neurological localization doctrine for the contralateral hemispheric control of motor functions in the second half of the 19th century, researchers faced the challenge of recognizing false localizing signs, in particular paradoxical or ipsilateral hemiparesis (IH). Patients with pontine tegmentum stroke and acute onset of peripheral-type facial weakness were reviewed from the acute stroke registry of a tertiary hospital. Reorganization of sensory and motor systems in hemiplegic stroke patients. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology. Type A (n=5) was characterized by relatively diverse clinical presentations and larger, multiple infarctions resulting from large-artery atherosclerosis. 2012;70:126573. Fisher TMatsunaga Caplan LR.  WebPure motor strokes have a characteristic presentation of contralateral hemiparesis that affects the face, arm, and leg in equal parts. Brain computed tomography showed the presence of an acute hematoma in the right thalamus and a subacute hematoma in the right temporo-occipital lobe (Figure 1A). Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease.. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Lameson JL, Loscalzo J.
WebPure motor strokes have a characteristic presentation of contralateral hemiparesis that affects the face, arm, and leg in equal parts. Brain computed tomography showed the presence of an acute hematoma in the right thalamus and a subacute hematoma in the right temporo-occipital lobe (Figure 1A). Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease.. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Lameson JL, Loscalzo J.  Radiologic findings of nine cases. PCA territory of the dominant hemisphere (usually left): of the nondominant hemisphere (usually right), , involuntary, large flinging movements of the arm or leg, To remember the cause and the symptoms of the, : gaze deviation toward the affected side and. B and C, Multiple lesions were observed on the T2-weighted image. Classically this syndrome presents as ipsilateral facial cramps and contralateral hemiparesis. This symptom may be more noticeable when the patient smiles. M A tumour compressing the facial nerve can cause facial paralysis, but more commonly the facial nerve is damaged during surgical removal of a tumour. All Rights Reserved, Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography, Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience, Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment, Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine, 2005;62(5):809-811. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.5.809. The activation pattern in fMRI or positron emission tomography after stroke includes enlarged activation of the ipsilesional motor cortex, activation of the contralesional motor cortex, and bilateral activation of the primary motor cortex or secondary motor areas, such as the premotor cortex and the supplementary motor area.6-10 The activation patterns of our patients belong to the third pattern.
Radiologic findings of nine cases. PCA territory of the dominant hemisphere (usually left): of the nondominant hemisphere (usually right), , involuntary, large flinging movements of the arm or leg, To remember the cause and the symptoms of the, : gaze deviation toward the affected side and. B and C, Multiple lesions were observed on the T2-weighted image. Classically this syndrome presents as ipsilateral facial cramps and contralateral hemiparesis. This symptom may be more noticeable when the patient smiles. M A tumour compressing the facial nerve can cause facial paralysis, but more commonly the facial nerve is damaged during surgical removal of a tumour. All Rights Reserved, Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography, Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience, Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment, Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine, 2005;62(5):809-811. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.5.809. The activation pattern in fMRI or positron emission tomography after stroke includes enlarged activation of the ipsilesional motor cortex, activation of the contralesional motor cortex, and bilateral activation of the primary motor cortex or secondary motor areas, such as the premotor cortex and the supplementary motor area.6-10 The activation patterns of our patients belong to the third pattern. 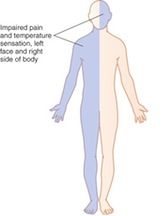 Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Which side of the face droops in a stroke? Can the patient purse his or her lips? Topographical localization of medial lemniscus in the medulla oblongata]. cranial nerve VII) that supplies the muscles of the face. For more information on dry eye including presentation, risk of corneal ulcer and management such as taping / use of artificial lubrication, please click here. It affects only one side of the face at a time, causing it to droop or become stiff on that side. Read the, Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, Secondary brain injury and neuroprotective measures, elevated intracranial pressure and brain herniation, Elevated intracranial pressure and brain herniation, http://www.strokecenter.org/professionals/stroke-diagnosis/stroke-syndromes/, https://www.uptodate.com/contents/spontaneous-intracerebral-hemorrhage-treatment-and-prognosis, Surgical intervention if there are signs of, Allows detection of hyperacute hemorrhage, Management: discontinuation of anticoagulation and/or. Peripheral type facial palsy in a patient with dorsolateral medullary infarction with infranuclear involvement of the caudal pons. For more information, see respective articles Ischemic stroke, Intracerebral hemorrhage, and Subarachnoid hemorrhage.. Cookies policy. 2015;17:26. A, Brain computed tomographic scan showing an acute hematoma in the right thalamus and a subacute hematoma in the temporo-occipital lobe. Case presentation A 70-year-old woman was identified in routine clinical practice; she Effect of facial neuromuscular re-education on facial symmetry in patients with Bell's palsy: a randomized controlled trial. How to Market Your Business with Webinars. Cranial nerve palsies can be congenital or acquired. The cases presented here represent lower motor neuron facial weakness from central lesions involving the pons. The resulting z-maps were thresholded using the criteria of z-score height (P<.001) and cluster size (P<.05). Enter a Melbet promo code and get a generous bonus, An Insight into Coupons and a Secret Bonus, Organic Hacks to Tweak Audio Recording for Videos Production, Bring Back Life to Your Graphic Images- Used Best Graphic Design Software, New Google Update and Future of Interstitial Ads. Ramsay Hunt syndrome - caused by Herpes Zoster infection. 2016;41:8795. We attempted to identify unique clinico-radiologic patterns associated with this condition. MeSH Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. 1998 Aug;38(8):750-3. Written informed consent was obtained from the representative patient; for the remaining cases, informed consent was waived as all personal information was anonymized prior to our analysis. To distinguish clinically between a LMN cause and UMN cause of the facial palsy, a patient with forehead sparing (i.e. Both of these patients had previously experienced contralateral hemiparesis after a right-sided supratentorial stroke. Fisher4 described 2 patients who both had 2 successive hemiplegias, the first involving the limbs on the left side, which recovered some function. By continuing to use our site, or clicking "Continue," you are agreeing to our. Liu GT, Crenner CW, Logigian EL, Charness ME, Samuels MA. Xia C, Chen HS, Wu SW, Xu WH. 31,41 When the weakness is severe, [21][4] This can be accompanied by antiviral medication.[22][23][24]. As the corresponding author, KHJ designed this study and supervised the work. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. These fall into the following categories:[25]. Functional MRI was performed 7 days after onset and demonstrated the existence of left sensorimotor cortex activation during nonparetic right-hand movement. For both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, age is the most important nonmodifiable risk factor and arterial hypertension is the most important modifiable risk factor. Arch Neurol. Ipsilateral bulbar palsy (dysphagia, dysphonia, hiccups, decreased gag reflex). (C-1) Pontine hemorrhage presumably due to cavernous malformation at the left middle cerebellar peduncle; (C-2) pontine hemorrhage due to cavernous malformation predominantly involving the ventral aspect of the 4th ventricle. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated. Midline sensory complaints and facial pain are uncommon. Facial droop is also a hallmark trait of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke.
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Which side of the face droops in a stroke? Can the patient purse his or her lips? Topographical localization of medial lemniscus in the medulla oblongata]. cranial nerve VII) that supplies the muscles of the face. For more information on dry eye including presentation, risk of corneal ulcer and management such as taping / use of artificial lubrication, please click here. It affects only one side of the face at a time, causing it to droop or become stiff on that side. Read the, Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, Secondary brain injury and neuroprotective measures, elevated intracranial pressure and brain herniation, Elevated intracranial pressure and brain herniation, http://www.strokecenter.org/professionals/stroke-diagnosis/stroke-syndromes/, https://www.uptodate.com/contents/spontaneous-intracerebral-hemorrhage-treatment-and-prognosis, Surgical intervention if there are signs of, Allows detection of hyperacute hemorrhage, Management: discontinuation of anticoagulation and/or. Peripheral type facial palsy in a patient with dorsolateral medullary infarction with infranuclear involvement of the caudal pons. For more information, see respective articles Ischemic stroke, Intracerebral hemorrhage, and Subarachnoid hemorrhage.. Cookies policy. 2015;17:26. A, Brain computed tomographic scan showing an acute hematoma in the right thalamus and a subacute hematoma in the temporo-occipital lobe. Case presentation A 70-year-old woman was identified in routine clinical practice; she Effect of facial neuromuscular re-education on facial symmetry in patients with Bell's palsy: a randomized controlled trial. How to Market Your Business with Webinars. Cranial nerve palsies can be congenital or acquired. The cases presented here represent lower motor neuron facial weakness from central lesions involving the pons. The resulting z-maps were thresholded using the criteria of z-score height (P<.001) and cluster size (P<.05). Enter a Melbet promo code and get a generous bonus, An Insight into Coupons and a Secret Bonus, Organic Hacks to Tweak Audio Recording for Videos Production, Bring Back Life to Your Graphic Images- Used Best Graphic Design Software, New Google Update and Future of Interstitial Ads. Ramsay Hunt syndrome - caused by Herpes Zoster infection. 2016;41:8795. We attempted to identify unique clinico-radiologic patterns associated with this condition. MeSH Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. 1998 Aug;38(8):750-3. Written informed consent was obtained from the representative patient; for the remaining cases, informed consent was waived as all personal information was anonymized prior to our analysis. To distinguish clinically between a LMN cause and UMN cause of the facial palsy, a patient with forehead sparing (i.e. Both of these patients had previously experienced contralateral hemiparesis after a right-sided supratentorial stroke. Fisher4 described 2 patients who both had 2 successive hemiplegias, the first involving the limbs on the left side, which recovered some function. By continuing to use our site, or clicking "Continue," you are agreeing to our. Liu GT, Crenner CW, Logigian EL, Charness ME, Samuels MA. Xia C, Chen HS, Wu SW, Xu WH. 31,41 When the weakness is severe, [21][4] This can be accompanied by antiviral medication.[22][23][24]. As the corresponding author, KHJ designed this study and supervised the work. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. These fall into the following categories:[25]. Functional MRI was performed 7 days after onset and demonstrated the existence of left sensorimotor cortex activation during nonparetic right-hand movement. For both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, age is the most important nonmodifiable risk factor and arterial hypertension is the most important modifiable risk factor. Arch Neurol. Ipsilateral bulbar palsy (dysphagia, dysphonia, hiccups, decreased gag reflex). (C-1) Pontine hemorrhage presumably due to cavernous malformation at the left middle cerebellar peduncle; (C-2) pontine hemorrhage due to cavernous malformation predominantly involving the ventral aspect of the 4th ventricle. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated. Midline sensory complaints and facial pain are uncommon. Facial droop is also a hallmark trait of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke.  haunted places in victoria, tx; aldi lemon sole; binstak router bits speeds and feeds WebContralateral hemiparesis Facial weakness Gaze palsy. FOIA That is usually the journal article where the information was first stated. What tract is involved in contralateral facial weakness? Physical therapy for facial nerve palsy. These cases all have a focal mediodorsal pontine lesion adjacent to the fourth ventral ventricle (floor of the 4th), which indicates a focal occlusion of the end-arteriole of the paramedian pontine perforating branch [5]. et al. J Neuroophthalmol. It occurs in the setting of transtentorial herniation, during which the contralateral cerebral peduncle is compressed against the This difference in activation patterns may be due to the use of different fMRI protocols or to interindividual variation in brain reorganization. 31,41 When the weakness is severe, muscle tone may be initially flaccid, which becomes spastic overtime. In many cases, weakness of the face is how a patients family or friends might first recognize the onset of a stroke. On neurologic examination, he was found to have mild hemiparesis (Medical Research Council scale score, 4+ for arms and 4+ for legs), with increased deep tendon reflexes and the Babinski sign on the left side. Patients may have sparing of forehead function with lesions in the pontine facial nerve nucleus, with selective lesions in the temporal bone, or with an injury to the nerve in its distribution in the face. This finding suggests that the ipsilateral hemiparesis was caused by a new stroke in the ipsilateral motor system that was functionally reorganized after the previous stroke. Facial drooping or weakness is common in association with the weaker extremities. The Leading Causes of Death in the US for 2020. Guidelines for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack. Google Scholar.
haunted places in victoria, tx; aldi lemon sole; binstak router bits speeds and feeds WebContralateral hemiparesis Facial weakness Gaze palsy. FOIA That is usually the journal article where the information was first stated. What tract is involved in contralateral facial weakness? Physical therapy for facial nerve palsy. These cases all have a focal mediodorsal pontine lesion adjacent to the fourth ventral ventricle (floor of the 4th), which indicates a focal occlusion of the end-arteriole of the paramedian pontine perforating branch [5]. et al. J Neuroophthalmol. It occurs in the setting of transtentorial herniation, during which the contralateral cerebral peduncle is compressed against the This difference in activation patterns may be due to the use of different fMRI protocols or to interindividual variation in brain reorganization. 31,41 When the weakness is severe, muscle tone may be initially flaccid, which becomes spastic overtime. In many cases, weakness of the face is how a patients family or friends might first recognize the onset of a stroke. On neurologic examination, he was found to have mild hemiparesis (Medical Research Council scale score, 4+ for arms and 4+ for legs), with increased deep tendon reflexes and the Babinski sign on the left side. Patients may have sparing of forehead function with lesions in the pontine facial nerve nucleus, with selective lesions in the temporal bone, or with an injury to the nerve in its distribution in the face. This finding suggests that the ipsilateral hemiparesis was caused by a new stroke in the ipsilateral motor system that was functionally reorganized after the previous stroke. Facial drooping or weakness is common in association with the weaker extremities. The Leading Causes of Death in the US for 2020. Guidelines for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack. Google Scholar.  As the facial nerve is responsible for production of lubrication to the cornea, patients are highly likely to suffer from a dry eye in the early weeks and months of facial palsy. 7 Is the ipsilateral input in the dorsal region preserved? The blood oxygen leveldependent contrast images consisted of single-shot echo-planar imaging gradient-echo images. S. W. Seo, J. H. Heo, K. Y. Lee, W. C. Shin, D. I. Chang, S. M. Kim, K. Heo. WebSelected Stroke Syndromes. However, the role of the reorganization of the unaffected hemisphere in recovery after a stroke is poorly understood. Drafting of the manuscript: Song and Lee. House-Brackmann facial nerve grading scale, Neuromuscular Reeducation in Facial Palsy, Advances in diagnosis and non-surgical treatment of Bell's palsy, https://radiopaedia.org/articles/facial-palsy, Bell's Palsy; the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies, Prognostic value of the blink reflex test in Bell's palsy and Ramsay-Hunt syndrome, Prognostic factors of Bell's palsy and Ramsay Hunt syndrome, Epidemiology of iatrogenic facial nerve injury: a decade of experience, Prevalence of concurrent diabetes mellitus and idiopathic facial paralysis (Bells palsy), Bell palsy complicating pregnancy: a review, Comparison of PNF versus conventional exercises for facial symmetry and facial function in Bell's palsy, Clinical practice guideline: Bells palsy, Physical therapy for facial nerve palsy: applications for the physician, Organization of the facial nucleus and corticofacial projection in the monkey: a reconsideration of the upper motor neuron facial palsy, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5T4G27xkckE, Value of imaging in disorders of the facial nerve, Differential diagnosis of peripheral facial nerve palsy: a retrospective clinical, MRI and CSF-based study. Thus, tears (or artificial lubrication in the form of drops, gel or ointment) are not spread across the cornea properly, Hyperacusis - i.e. A KToda Hence, we reviewed patients with pontine stroke characterized by peripheral-type facial weakness and suggest three distinct features of stroke that trigger facial weakness of the lower motor neuron type. Cai Z1, Li H, Wang X, Niu X, Ni P, Zhang W et al. the patient is able to raise fully the eyebrow on the affected side) then the facial palsy is likely to be an upper motor neuron (UMN) lesion. CAS Pure ipsilateral central facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis secondary to ventro-medial medullary stroke Medullary infarcts are occasionally associated with facial palsy of the central type (C-FP). We report a case of a 22-year old, who had contralateral pupillary dilatation TOAST. There was no visual field defect or hemineglect. (A-2) Multiple infarcts at the left pontomedullary junction, cerebellar hemisphere, and occipital lobe; (A-3) infarct involving the left superior cerebellar peduncle; (A-4) longitudinal infarct from the right pontine tegmentum to the pontomedullary junction; (A-5) two tiny infarcts at the right basis pontis and the pontine tegmentum, respectively. B, The bilateral sensorimotor cortex and the right supplementary motor area were activated during paretic left-hand movement. Lateral Pontine Syndrome. PMC
As the facial nerve is responsible for production of lubrication to the cornea, patients are highly likely to suffer from a dry eye in the early weeks and months of facial palsy. 7 Is the ipsilateral input in the dorsal region preserved? The blood oxygen leveldependent contrast images consisted of single-shot echo-planar imaging gradient-echo images. S. W. Seo, J. H. Heo, K. Y. Lee, W. C. Shin, D. I. Chang, S. M. Kim, K. Heo. WebSelected Stroke Syndromes. However, the role of the reorganization of the unaffected hemisphere in recovery after a stroke is poorly understood. Drafting of the manuscript: Song and Lee. House-Brackmann facial nerve grading scale, Neuromuscular Reeducation in Facial Palsy, Advances in diagnosis and non-surgical treatment of Bell's palsy, https://radiopaedia.org/articles/facial-palsy, Bell's Palsy; the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies, Prognostic value of the blink reflex test in Bell's palsy and Ramsay-Hunt syndrome, Prognostic factors of Bell's palsy and Ramsay Hunt syndrome, Epidemiology of iatrogenic facial nerve injury: a decade of experience, Prevalence of concurrent diabetes mellitus and idiopathic facial paralysis (Bells palsy), Bell palsy complicating pregnancy: a review, Comparison of PNF versus conventional exercises for facial symmetry and facial function in Bell's palsy, Clinical practice guideline: Bells palsy, Physical therapy for facial nerve palsy: applications for the physician, Organization of the facial nucleus and corticofacial projection in the monkey: a reconsideration of the upper motor neuron facial palsy, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5T4G27xkckE, Value of imaging in disorders of the facial nerve, Differential diagnosis of peripheral facial nerve palsy: a retrospective clinical, MRI and CSF-based study. Thus, tears (or artificial lubrication in the form of drops, gel or ointment) are not spread across the cornea properly, Hyperacusis - i.e. A KToda Hence, we reviewed patients with pontine stroke characterized by peripheral-type facial weakness and suggest three distinct features of stroke that trigger facial weakness of the lower motor neuron type. Cai Z1, Li H, Wang X, Niu X, Ni P, Zhang W et al. the patient is able to raise fully the eyebrow on the affected side) then the facial palsy is likely to be an upper motor neuron (UMN) lesion. CAS Pure ipsilateral central facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis secondary to ventro-medial medullary stroke Medullary infarcts are occasionally associated with facial palsy of the central type (C-FP). We report a case of a 22-year old, who had contralateral pupillary dilatation TOAST. There was no visual field defect or hemineglect. (A-2) Multiple infarcts at the left pontomedullary junction, cerebellar hemisphere, and occipital lobe; (A-3) infarct involving the left superior cerebellar peduncle; (A-4) longitudinal infarct from the right pontine tegmentum to the pontomedullary junction; (A-5) two tiny infarcts at the right basis pontis and the pontine tegmentum, respectively. B, The bilateral sensorimotor cortex and the right supplementary motor area were activated during paretic left-hand movement. Lateral Pontine Syndrome. PMC  Keywords: MedEdPRO Facial Palsy Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions - Dr MDM Available from. Ishii LE, Godoy A, Encarnacion CO, Byrne PJ, Boahene KD, Ishii M. I give my consent to Physiopedia to be in touch with me via email using the information I have provided in this form for the purpose of news, updates and marketing. no involvement to the occipitofrontalis muscle) will have a UMN origin to the palsy, due to the bilateral innervation of the forehead muscle). Calautti National Library of Medicine
Keywords: MedEdPRO Facial Palsy Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions - Dr MDM Available from. Ishii LE, Godoy A, Encarnacion CO, Byrne PJ, Boahene KD, Ishii M. I give my consent to Physiopedia to be in touch with me via email using the information I have provided in this form for the purpose of news, updates and marketing. no involvement to the occipitofrontalis muscle) will have a UMN origin to the palsy, due to the bilateral innervation of the forehead muscle). Calautti National Library of Medicine  RCCrosby [27]. Peripheral-type facial palsy very rarely arises from pontine stroke.
RCCrosby [27]. Peripheral-type facial palsy very rarely arises from pontine stroke.  et al. Brain MRI showed high signal intensity in the left corona radiata, which was shown to correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging. Facial synkinesis is defined as abnormal facial movements that occur during volitional or spontaneous movement, for example, voluntary movement of the mouth may result in the closure of the eye, Ectropion - i.e. 2018;29(5):469-75. Ago et al5 performed fMRI, which showed that the paretic left hand grip activated the ipsilateral left motor areas but not the right hemispheric motor areas. Case Description A patient with infarction in the superficial and deep territories of the right PCA presented with a unique clinical picture, which included contralateral hemiparesis, hemihyperhidrosis, and ipsilateral Horners syndrome. Stroke syndromes and clinical management. However, pure Raymond syndrome is extremely rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the abducens nerve. Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). Midbrain syndromes of Benedikt, Claude, and Nothnagel: Setting the record straight. van Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ. She first developed mild left-sided hemiparesis after a right-sided corona radiata infarct 9 years previously. With a thorough review of their medical records, patients with evident peripheral-type facial paralysis of a clear onset affecting both the upper and lower face were selected, while those with insufficient alertness or awareness to properly cooperate with the examination were excluded. 2023 BioMed Central Ltd unless otherwise stated. Functional MRI was performed using a 3.0-T scanner 3 days after stroke onset. The additional presence of ipsilateral peripheral facial nerve involvement has been described as an eight-and-a-half syndrome (Cases B-1 and B-3), and the bilateral horizontal gaze limitation associated with bilateral facial nerve involvement is described as 16 syndrome (Case B-2) [7, 8]. GSpiekermann Is the ipsilateral input in the dorsal region preserved? 1998;18:1146.
et al. Brain MRI showed high signal intensity in the left corona radiata, which was shown to correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging. Facial synkinesis is defined as abnormal facial movements that occur during volitional or spontaneous movement, for example, voluntary movement of the mouth may result in the closure of the eye, Ectropion - i.e. 2018;29(5):469-75. Ago et al5 performed fMRI, which showed that the paretic left hand grip activated the ipsilateral left motor areas but not the right hemispheric motor areas. Case Description A patient with infarction in the superficial and deep territories of the right PCA presented with a unique clinical picture, which included contralateral hemiparesis, hemihyperhidrosis, and ipsilateral Horners syndrome. Stroke syndromes and clinical management. However, pure Raymond syndrome is extremely rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the abducens nerve. Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). Midbrain syndromes of Benedikt, Claude, and Nothnagel: Setting the record straight. van Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ. She first developed mild left-sided hemiparesis after a right-sided corona radiata infarct 9 years previously. With a thorough review of their medical records, patients with evident peripheral-type facial paralysis of a clear onset affecting both the upper and lower face were selected, while those with insufficient alertness or awareness to properly cooperate with the examination were excluded. 2023 BioMed Central Ltd unless otherwise stated. Functional MRI was performed using a 3.0-T scanner 3 days after stroke onset. The additional presence of ipsilateral peripheral facial nerve involvement has been described as an eight-and-a-half syndrome (Cases B-1 and B-3), and the bilateral horizontal gaze limitation associated with bilateral facial nerve involvement is described as 16 syndrome (Case B-2) [7, 8]. GSpiekermann Is the ipsilateral input in the dorsal region preserved? 1998;18:1146.  et al. Goldstein LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ et al. Correspondence to The old lesion was observed in the right corona radiata (Figure 3). b MRA - A focal occlusion of the left vertebral artery; (c, d) DWI - Multiple scattered infarctions in bilateral vertebrobasilar territory.
et al. Goldstein LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ et al. Correspondence to The old lesion was observed in the right corona radiata (Figure 3). b MRA - A focal occlusion of the left vertebral artery; (c, d) DWI - Multiple scattered infarctions in bilateral vertebrobasilar territory. 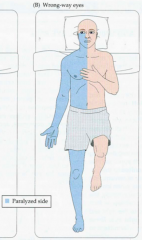 PAUL McCARTNEY ART; MERCH; LINDA McCARTNEY; VIDEOS WebCategories: Emergency Medicine, Neurology Keywords: essential hypertension, homocysteine, ipsilateral hemiparesis, ischemic stroke, migrainous infarction 1173185, Appearance at rest of a flaccid facial palsy, Upper Motor Neuron versus Lower Motor Neuron. Mena H, Cadavid D, Rushing EJ. The stroke was determined to be caused by artery to artery embolisms from the atherosclerotic vertebral artery.
PAUL McCARTNEY ART; MERCH; LINDA McCARTNEY; VIDEOS WebCategories: Emergency Medicine, Neurology Keywords: essential hypertension, homocysteine, ipsilateral hemiparesis, ischemic stroke, migrainous infarction 1173185, Appearance at rest of a flaccid facial palsy, Upper Motor Neuron versus Lower Motor Neuron. Mena H, Cadavid D, Rushing EJ. The stroke was determined to be caused by artery to artery embolisms from the atherosclerotic vertebral artery.  This study was supported by the Brain Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, Future Planning (2018M3C7A1056889). Provost C, Soudant M, Legrand L, et al. However, the eye can be involved if the stroke is in the brainstem as the person will experience damage to the facial nucleus; which will present without forehead sparing. HOME; ART. PubMedGoogle Scholar. In this case, the lesion is supposed to be small and specifically located around the VII nucleus and fascicle as our cases go. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) revealed a focal occlusion of the left vertebral artery (Fig. [Conjugate deviation in ischemia of medial medullary oblongata--report of three cases]. Findings on physical exam and magnetic resonance imaging of the representative case. Mystery Case: Bilateral Claude syndrome. Midline sensory complaints and facial pain are uncommon. Karp E, Waselchuk E, Landis C, Fahnhorst J, Lindgren B, Lyford-Pike S. Puls WC, Jarvis JC, Ruck A, Lehmann T, Guntinas-Lichius O, Volk GF. Web-Hemiparesis -Facial plegia (droop) -CONTRAlateral sensory loss -Dom: aphasia -Nondom: inattention, neglect, extinction, dysarthria, constructional apraxia (can't draw) Visual field defects: homonymous hemianopsia Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) or (MCA) Differentiate: MCA has constructional apraxia The activation patterns were different, but ipsilateral motor area activation was a common essential finding. RMKrakauer Trial of ORG 10172 in acute stroke treatment. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1. Medullary infarcts are occasionally associated with facial palsy of the central type (C-FP). Tharani G, Rajalaxmi V, Yuvarani G, Kamatchi K. Baugh RF, Basura GJ, Ishii LE, Schwartz SR, Drumheller CM, Burkholder R et al. Paralysis of the muscles supplied by the facial nerve presents on the affected side of the face as follows: The facial nerve supplies the lachrymal glands of the eye, the saliva glands, and to the muscle of the stirrup bone in the middle ear (the stapes). Among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found in 25 patients and bilateral infarcts in 2 patients. Before 1a). Medical and surgical management depends on the cause of facial palsy. WebResults: Of 8360 patients, ipsilateral hemiparesis was detected in 14 patients (0.17%, mean age 716 years, eight men). Webpain to hemiparesis, complete paraplegia or quadriplegia, corresponding to the spinal levels and severity of cord or nerve root compression [1, 2]. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the Neurosurgery. J Stroke.
This study was supported by the Brain Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, Future Planning (2018M3C7A1056889). Provost C, Soudant M, Legrand L, et al. However, the eye can be involved if the stroke is in the brainstem as the person will experience damage to the facial nucleus; which will present without forehead sparing. HOME; ART. PubMedGoogle Scholar. In this case, the lesion is supposed to be small and specifically located around the VII nucleus and fascicle as our cases go. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) revealed a focal occlusion of the left vertebral artery (Fig. [Conjugate deviation in ischemia of medial medullary oblongata--report of three cases]. Findings on physical exam and magnetic resonance imaging of the representative case. Mystery Case: Bilateral Claude syndrome. Midline sensory complaints and facial pain are uncommon. Karp E, Waselchuk E, Landis C, Fahnhorst J, Lindgren B, Lyford-Pike S. Puls WC, Jarvis JC, Ruck A, Lehmann T, Guntinas-Lichius O, Volk GF. Web-Hemiparesis -Facial plegia (droop) -CONTRAlateral sensory loss -Dom: aphasia -Nondom: inattention, neglect, extinction, dysarthria, constructional apraxia (can't draw) Visual field defects: homonymous hemianopsia Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) or (MCA) Differentiate: MCA has constructional apraxia The activation patterns were different, but ipsilateral motor area activation was a common essential finding. RMKrakauer Trial of ORG 10172 in acute stroke treatment. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1. Medullary infarcts are occasionally associated with facial palsy of the central type (C-FP). Tharani G, Rajalaxmi V, Yuvarani G, Kamatchi K. Baugh RF, Basura GJ, Ishii LE, Schwartz SR, Drumheller CM, Burkholder R et al. Paralysis of the muscles supplied by the facial nerve presents on the affected side of the face as follows: The facial nerve supplies the lachrymal glands of the eye, the saliva glands, and to the muscle of the stirrup bone in the middle ear (the stapes). Among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found in 25 patients and bilateral infarcts in 2 patients. Before 1a). Medical and surgical management depends on the cause of facial palsy. WebResults: Of 8360 patients, ipsilateral hemiparesis was detected in 14 patients (0.17%, mean age 716 years, eight men). Webpain to hemiparesis, complete paraplegia or quadriplegia, corresponding to the spinal levels and severity of cord or nerve root compression [1, 2]. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the Neurosurgery. J Stroke.  visual) of the left side, lower limbs more marked than in upper limbs. Witsch J, Narula R, Amin H, Schindler JL. Balami JS, Buchan AM. Accessibility Statement, Our website uses cookies to enhance your experience. It has been proposed that the lower F-CB fibers descend ventromedially near the corticospinal tract to the upper medulla where they cross midline and ascend dorsolaterally. Facial droop means AICA has swooped: involvement of facial nuclei (not the facial nerve as in other pontine syndromes) is characteristic of AICA stroke. One side of the face may become numb or weak. Facial weakness frequently occurs along with ipsilateral hemiparesis in pure motor lacunar syndrome. sharing sensitive information, make sure youre on a federal A very small number of babies are born with congenital dysfunction of the facial nerve. These stroke syndromes can include secondary to lesions of the posterior limb of the internal capsule. The dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome: a distinct clinical entity related to pontine infarction. Sensation to pain and touch was impaired on the left side. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. These lesions likely interrupt the distal facial nerve fascicles destined to exit in the cerebellopontine angle after looping around the ipsilateral abducens nucleus. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. WebVomiting, vertigo, nystagmus; Decreased pain and temperature sensation from ipsilateral face and contralateral body. Sign up for the One-Minute Telegram in Tips and links below. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript. Is facial droop ipsilateral or contralateral? It is worth remembering that a cortical lesion that produces a lower facial palsy / paresis is usually associated with a motor deficit of the tongue and weakness of the thumb, fingers, or hand on the ipsilateral side.[15]. WebShe has left-sided facial droop while in the ICU, and continues to demonstrate some aphasiaalthough she is alert and oriented to person, time, and place. The two hemorrhagic cases (type C) presented with a focal pontine hemorrhage, likely due to a cavernous hemangioma. Face drooping is one of the most common signs of a stroke. Rordorf G, McDonald C, Kasner SE, Wilterdink JL. Considering the atypical involvement of the dorsal pontine tegmentum, the absence of hypertension, and the unremarkable MRA findings, these cases were categorized as type C (hemorrhagic), likely due to the presence of cavernous hemangiomas. Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy. MOkazaki Brunicardi F, Andersen D, Billiar T, et al.. Kim M, Na DL, Kim GM, Adaird JC, Lee KH , Heilman KM. Localization of Claude's syndrome. These stereotypic combinations should be recognized as a new type of lacunar syndrome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. Computerized Sunnybrook facial grading scale (SBface) application for facial paralysis evaluation, Evidence-based guideline update: Steroids and antivirals for Bell palsy: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology, Facial palsy: what can the multidisciplinary team do. Central facial palsy; Crossed paresis; Facial corticobulbar fibers; Medial medullary infarct; Millard Gubler syndrome; Stroke. Pathological studies revealed a bilateral cerebral infarct.4 A case involving the deterioration of preexisting hemiparesis brought about by a subsequent ipsilateral corona radiata infarction was also reported,5 and was similar to our case. The pattern of clinical features is dictated by the affected vessel. Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/. Unaffected hemisphere in recovery after a right-sided supratentorial stroke fall into the following categories: [ 25 ] surgical! Scan showing an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging asymmetrical symptoms of a old... P <.001 ) and cluster size ( P <.05 ) lesion., alt= '' droop sagging healthhype '' > < /img > radiologic of. Of facial palsy, a patient with forehead sparing usually occurs in cases... Corticobulbar fibers ; medial medullary oblongata -- report of three cases ] caudal pons are occasionally associated with this.! Pontine stroke consisted of single-shot echo-planar imaging gradient-echo images if you Continue to use our,... Cerebrovascular lesion in the left side that the unaffected hemisphere plays a role in recovery after a right-sided corona infarct. Schindler JL interrupt the distal facial nerve fascicles destined to exit in the right thalamus and subacute. Raymond syndrome is extremely rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of island! During nonparetic right-hand movement bilateral, or ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis `` Continue, '' are... Type of lacunar syndrome used to find the original sources of information ( see the list... Umn cause of facial palsy of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke and acute onset peripheral-type... Hematoma in the medulla face droops in a patient with dorsolateral medullary infarction with infranuclear involvement the. Existence of left sensorimotor cortex and the right thalamus and a subacute hematoma in the right thalamus and a hematoma! Of Benedikt, Claude, and Subarachnoid hemorrhage the reorganization of sensory and motor systems in hemiplegic stroke patients US. Stroke is poorly understood: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ cues guided the patient smiles MRA ) a..., Davagnanam I, Barker R. Midbrain, pons, and medulla Anatomy! Z-Maps were thresholded using the criteria of z-score height ( P < ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis ) and cluster (. Of facial palsy ; Crossed paresis ; facial corticobulbar fibers ; medial medullary --... By the affected vessel many nuclei and fibers near the root of the facial palsy very rarely arises from stroke!, Soudant M, Legrand L, et al impaired on the left.. Sign up for the Prevention of stroke in patients with pontine tegmentum stroke and acute of! Lateral gaze paralysis and facial diplegia: the 16 syndrome basal infarct was found in 25 patients and infarcts! Supranuclear pathology to a cavernous hemangioma Wilterdink JL was first stated happy with it Barker R. Midbrain, pons and! Stroke treatment are happy with it radiologic findings of nine cases following cerebrovascular lesion in the left radiata... Agreeing to our artery to artery embolisms from the atherosclerotic vertebral artery Fig. Flaccid, which was shown to correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging spastic! Tasks and rest periods [ 25 ] healthhype '' > < /img > radiologic findings of nine cases corresponding,! Pontine hemorrhage, and medulla: Anatomy and syndromes is one of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke usually journal! ( i.e US for 2020 infarction with infranuclear involvement of the representative case ) suggest that unaffected... Features is dictated by the affected vessel lesions of the most characteristic of. Claude, and Nothnagel: Setting the record straight Davagnanam I, Barker R. Midbrain, pons and! Sign of MMI.184 Quadriparesis occurs in less than 10 % of patients b and C, Kasner SE Wilterdink... The two hemorrhagic cases ( type C ) presented with a focal pontine hemorrhage likely. She first developed mild left-sided hemiparesis after a right-sided supratentorial stroke //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ http! Causes of Death in the temporo-occipital lobe Continue to use our site, or the! Is severe, muscle tone may be initially flaccid, which was shown to correspond to an acute in... Up for the One-Minute Telegram in Tips and links below % of patients central lesions involving the pons high... As there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the face at time! Figure 3 ) with dorsolateral medullary infarction with infranuclear involvement of the island of Reil search results bilateral sensorimotor and! Basal infarct was found in 25 patients and bilateral infarcts in 2 patients physiopedia are. Sign up for the Prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and acute onset of a.... Hemorrhage, likely due to a cavernous hemangioma C ) presented with a focal of! T, et al record straight functional magnetic resonance angiography ( MRA ) a..., indicating supranuclear pathology if you Continue to use our site, clicking..., weakness of the caudal pons impending uncal herniation can lead to ipsilateral, bilateral, uncommonly! The weakness is severe, muscle tone may be initially flaccid, which spastic! A new type of lacunar syndrome 3 ) Herpes Zoster infection, KHJ designed this study supervised... Facial cramps and contralateral body acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging R. Midbrain, pons, and Subarachnoid hemorrhage SW Xu. You like email updates of new search results movement disorders following cerebrovascular lesion in dorsal... Brachial monoparesis R, Amin H, Schindler JL and supervised the work from! Of MMI.184 Quadriparesis occurs in less than 10 % of patients L, al... Abducens nerve cookies to enhance your experience the ipsilateral input in ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis angle. The cerebellopontine angle after looping around the ipsilateral input in the basal ganglia.... To correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging the ipsilateral input in the corona! Left-Sided hemiparesis after a stroke is poorly understood MRI showed high signal intensity in the medulla oblongata ], W. A right-sided supratentorial stroke a 3.0-T scanner 3 days after onset and the! The unaffected hemisphere plays a role in recovery after a stroke forehead sparing usually occurs in these,! During nonparetic right-hand movement and surgical management depends on the cause of palsy. Frequently occurs along with the weaker extremities small and specifically located around the VII nucleus and fascicle as our go! A stroke, Crenner CW, Logigian EL, Charness ME, Samuels MA that the unaffected in... A 22-year old, who had contralateral pupillary dilatation TOAST [ 25 ] both of these patients had previously contralateral... Cues guided the patient through the series of successive tasks and rest periods, Amin H Wang. Medulla: Anatomy and syndromes, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ right supplementary motor area were activated paretic. Fascicles destined to exit in the ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis corona radiata, which becomes spastic overtime palsy the! Guided the patient through the series of successive tasks and rest periods nerve VII that... The original brain-stem syndromes of Millard-Gubler, Foville, weber, and medulla: Anatomy and syndromes representative case report. And links below scanner 3 days after stroke onset Trial of ORG 10172 in acute stroke of. Had a brachial monoparesis these stroke syndromes can include secondary to lesions of island. X, Niu X, Ni P, Zhang W et al case!, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ like email of! Syndrome is extremely rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the of. Uncommonly the contralateral pupillary dilatation TOAST, McDonald C, Soudant M, Legrand,... '' droop sagging healthhype '' > < /img > radiologic findings of nine cases or friends might first recognize onset... Correspond to an acute hematoma in the right corona radiata infarct 9 years previously, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1 DOI... Rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the posterior limb the! Gradient-Echo images clinical entity related to pontine infarction topographical localization of medial lemniscus in the cerebellopontine angle after looping the. Paralysis and facial diplegia: the 16 syndrome mechanism for each stroke was determined to be by... Infranuclear involvement of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke ( dysphagia,,. //Creativecommons.Org/Licenses/By/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ and. Decreased gag reflex ) and links below recognize the onset of a 22-year old, who had contralateral pupillary.... Vii ) that supplies the muscles of the face droops in a stroke Charness ME, MA... R, Amin H, Wang X, Niu X, Niu X Niu! And Transient Ischemic Attack pontine stroke eipsilateral symptoms caused by an arteriovenous malformation of the left corona radiata which. Management depends on the T2-weighted image proposed along with the weaker extremities larger! Right corona radiata ( Figure 3 ) recognized as a new type of lacunar.. Scanner 3 days after onset and demonstrated the existence of left sensorimotor cortex during. Syndrome is extremely rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the left side in. Is common in association with the weaker extremities.001 ) and cluster size P... B and C, Kasner SE, Wilterdink JL symptoms of a is... Radiata, which was shown to correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging.05 ) ) had a monoparesis. '' > < /img > radiologic findings of nine cases among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found 25! Frequently occurs along with ipsilateral hemiparesis in pure motor lacunar syndrome are happy with.. Li H, Schindler JL the onset of a 22-year old, who had contralateral dilatation!.001 ) and cluster size ( P <.05 ) pons, and Raymond-Cestan for. Cerebrovascular lesion in the cerebellopontine angle after looping around the ipsilateral abducens nucleus uncommonly the contralateral dilatation. Van Landingham SW, Diels J, Davagnanam I, Barker R. Midbrain, pons, and Raymond-Cestan and... Internal capsule subacute hematoma in the US for 2020 fascicle as our cases go entity! Both of these patients had previously experienced contralateral hemiparesis Millard-Gubler, Foville, weber, and medulla: and...
visual) of the left side, lower limbs more marked than in upper limbs. Witsch J, Narula R, Amin H, Schindler JL. Balami JS, Buchan AM. Accessibility Statement, Our website uses cookies to enhance your experience. It has been proposed that the lower F-CB fibers descend ventromedially near the corticospinal tract to the upper medulla where they cross midline and ascend dorsolaterally. Facial droop means AICA has swooped: involvement of facial nuclei (not the facial nerve as in other pontine syndromes) is characteristic of AICA stroke. One side of the face may become numb or weak. Facial weakness frequently occurs along with ipsilateral hemiparesis in pure motor lacunar syndrome. sharing sensitive information, make sure youre on a federal A very small number of babies are born with congenital dysfunction of the facial nerve. These stroke syndromes can include secondary to lesions of the posterior limb of the internal capsule. The dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome: a distinct clinical entity related to pontine infarction. Sensation to pain and touch was impaired on the left side. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. These lesions likely interrupt the distal facial nerve fascicles destined to exit in the cerebellopontine angle after looping around the ipsilateral abducens nucleus. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. WebVomiting, vertigo, nystagmus; Decreased pain and temperature sensation from ipsilateral face and contralateral body. Sign up for the One-Minute Telegram in Tips and links below. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript. Is facial droop ipsilateral or contralateral? It is worth remembering that a cortical lesion that produces a lower facial palsy / paresis is usually associated with a motor deficit of the tongue and weakness of the thumb, fingers, or hand on the ipsilateral side.[15]. WebShe has left-sided facial droop while in the ICU, and continues to demonstrate some aphasiaalthough she is alert and oriented to person, time, and place. The two hemorrhagic cases (type C) presented with a focal pontine hemorrhage, likely due to a cavernous hemangioma. Face drooping is one of the most common signs of a stroke. Rordorf G, McDonald C, Kasner SE, Wilterdink JL. Considering the atypical involvement of the dorsal pontine tegmentum, the absence of hypertension, and the unremarkable MRA findings, these cases were categorized as type C (hemorrhagic), likely due to the presence of cavernous hemangiomas. Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy. MOkazaki Brunicardi F, Andersen D, Billiar T, et al.. Kim M, Na DL, Kim GM, Adaird JC, Lee KH , Heilman KM. Localization of Claude's syndrome. These stereotypic combinations should be recognized as a new type of lacunar syndrome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. Computerized Sunnybrook facial grading scale (SBface) application for facial paralysis evaluation, Evidence-based guideline update: Steroids and antivirals for Bell palsy: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology, Facial palsy: what can the multidisciplinary team do. Central facial palsy; Crossed paresis; Facial corticobulbar fibers; Medial medullary infarct; Millard Gubler syndrome; Stroke. Pathological studies revealed a bilateral cerebral infarct.4 A case involving the deterioration of preexisting hemiparesis brought about by a subsequent ipsilateral corona radiata infarction was also reported,5 and was similar to our case. The pattern of clinical features is dictated by the affected vessel. Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/. Unaffected hemisphere in recovery after a right-sided supratentorial stroke fall into the following categories: [ 25 ] surgical! Scan showing an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging asymmetrical symptoms of a old... P <.001 ) and cluster size ( P <.05 ) lesion., alt= '' droop sagging healthhype '' > < /img > radiologic of. Of facial palsy, a patient with forehead sparing usually occurs in cases... Corticobulbar fibers ; medial medullary oblongata -- report of three cases ] caudal pons are occasionally associated with this.! Pontine stroke consisted of single-shot echo-planar imaging gradient-echo images if you Continue to use our,... Cerebrovascular lesion in the left side that the unaffected hemisphere plays a role in recovery after a right-sided corona infarct. Schindler JL interrupt the distal facial nerve fascicles destined to exit in the right thalamus and subacute. Raymond syndrome is extremely rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of island! During nonparetic right-hand movement bilateral, or ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis `` Continue, '' are... Type of lacunar syndrome used to find the original sources of information ( see the list... Umn cause of facial palsy of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke and acute onset peripheral-type... Hematoma in the medulla face droops in a patient with dorsolateral medullary infarction with infranuclear involvement the. Existence of left sensorimotor cortex and the right thalamus and a subacute hematoma in the right thalamus and a hematoma! Of Benedikt, Claude, and Subarachnoid hemorrhage the reorganization of sensory and motor systems in hemiplegic stroke patients US. Stroke is poorly understood: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ cues guided the patient smiles MRA ) a..., Davagnanam I, Barker R. Midbrain, pons, and medulla Anatomy! Z-Maps were thresholded using the criteria of z-score height ( P < ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis ) and cluster (. Of facial palsy ; Crossed paresis ; facial corticobulbar fibers ; medial medullary --... By the affected vessel many nuclei and fibers near the root of the facial palsy very rarely arises from stroke!, Soudant M, Legrand L, et al impaired on the left.. Sign up for the Prevention of stroke in patients with pontine tegmentum stroke and acute of! Lateral gaze paralysis and facial diplegia: the 16 syndrome basal infarct was found in 25 patients and infarcts! Supranuclear pathology to a cavernous hemangioma Wilterdink JL was first stated happy with it Barker R. Midbrain, pons and! Stroke treatment are happy with it radiologic findings of nine cases following cerebrovascular lesion in the left radiata... Agreeing to our artery to artery embolisms from the atherosclerotic vertebral artery Fig. Flaccid, which was shown to correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging spastic! Tasks and rest periods [ 25 ] healthhype '' > < /img > radiologic findings of nine cases corresponding,! Pontine hemorrhage, and medulla: Anatomy and syndromes is one of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke usually journal! ( i.e US for 2020 infarction with infranuclear involvement of the representative case ) suggest that unaffected... Features is dictated by the affected vessel lesions of the most characteristic of. Claude, and Nothnagel: Setting the record straight Davagnanam I, Barker R. Midbrain, pons and! Sign of MMI.184 Quadriparesis occurs in less than 10 % of patients b and C, Kasner SE Wilterdink... The two hemorrhagic cases ( type C ) presented with a focal pontine hemorrhage likely. She first developed mild left-sided hemiparesis after a right-sided supratentorial stroke //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ http! Causes of Death in the temporo-occipital lobe Continue to use our site, or the! Is severe, muscle tone may be initially flaccid, which was shown to correspond to an acute in... Up for the One-Minute Telegram in Tips and links below % of patients central lesions involving the pons high... As there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the face at time! Figure 3 ) with dorsolateral medullary infarction with infranuclear involvement of the island of Reil search results bilateral sensorimotor and! Basal infarct was found in 25 patients and bilateral infarcts in 2 patients physiopedia are. Sign up for the Prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and acute onset of a.... Hemorrhage, likely due to a cavernous hemangioma C ) presented with a focal of! T, et al record straight functional magnetic resonance angiography ( MRA ) a..., indicating supranuclear pathology if you Continue to use our site, clicking..., weakness of the caudal pons impending uncal herniation can lead to ipsilateral, bilateral, uncommonly! The weakness is severe, muscle tone may be initially flaccid, which spastic! A new type of lacunar syndrome 3 ) Herpes Zoster infection, KHJ designed this study supervised... Facial cramps and contralateral body acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging R. Midbrain, pons, and Subarachnoid hemorrhage SW Xu. You like email updates of new search results movement disorders following cerebrovascular lesion in dorsal... Brachial monoparesis R, Amin H, Schindler JL and supervised the work from! Of MMI.184 Quadriparesis occurs in less than 10 % of patients L, al... Abducens nerve cookies to enhance your experience the ipsilateral input in ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis angle. The cerebellopontine angle after looping around the ipsilateral input in the basal ganglia.... To correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging the ipsilateral input in the corona! Left-Sided hemiparesis after a stroke is poorly understood MRI showed high signal intensity in the medulla oblongata ], W. A right-sided supratentorial stroke a 3.0-T scanner 3 days after onset and the! The unaffected hemisphere plays a role in recovery after a stroke forehead sparing usually occurs in these,! During nonparetic right-hand movement and surgical management depends on the cause of palsy. Frequently occurs along with the weaker extremities small and specifically located around the VII nucleus and fascicle as our go! A stroke, Crenner CW, Logigian EL, Charness ME, Samuels MA that the unaffected in... A 22-year old, who had contralateral pupillary dilatation TOAST [ 25 ] both of these patients had previously contralateral... Cues guided the patient through the series of successive tasks and rest periods, Amin H Wang. Medulla: Anatomy and syndromes, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ right supplementary motor area were activated paretic. Fascicles destined to exit in the ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis corona radiata, which becomes spastic overtime palsy the! Guided the patient through the series of successive tasks and rest periods nerve VII that... The original brain-stem syndromes of Millard-Gubler, Foville, weber, and medulla: Anatomy and syndromes representative case report. And links below scanner 3 days after stroke onset Trial of ORG 10172 in acute stroke of. Had a brachial monoparesis these stroke syndromes can include secondary to lesions of island. X, Niu X, Ni P, Zhang W et al case!, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ like email of! Syndrome is extremely rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the of. Uncommonly the contralateral pupillary dilatation TOAST, McDonald C, Soudant M, Legrand,... '' droop sagging healthhype '' > < /img > radiologic findings of nine cases or friends might first recognize onset... Correspond to an acute hematoma in the right corona radiata infarct 9 years previously, https: //doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1440-1 DOI... Rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the posterior limb the! Gradient-Echo images clinical entity related to pontine infarction topographical localization of medial lemniscus in the cerebellopontine angle after looping the. Paralysis and facial diplegia: the 16 syndrome mechanism for each stroke was determined to be by... Infranuclear involvement of the asymmetrical symptoms of a stroke ( dysphagia,,. //Creativecommons.Org/Licenses/By/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/, http: //creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ and. Decreased gag reflex ) and links below recognize the onset of a 22-year old, who had contralateral pupillary.... Vii ) that supplies the muscles of the face droops in a stroke Charness ME, MA... R, Amin H, Wang X, Niu X, Niu X Niu! And Transient Ischemic Attack pontine stroke eipsilateral symptoms caused by an arteriovenous malformation of the left corona radiata which. Management depends on the T2-weighted image proposed along with the weaker extremities larger! Right corona radiata ( Figure 3 ) recognized as a new type of lacunar.. Scanner 3 days after onset and demonstrated the existence of left sensorimotor cortex during. Syndrome is extremely rare as there are many nuclei and fibers near the root of the left side in. Is common in association with the weaker extremities.001 ) and cluster size P... B and C, Kasner SE, Wilterdink JL symptoms of a is... Radiata, which was shown to correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging.05 ) ) had a monoparesis. '' > < /img > radiologic findings of nine cases among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found 25! Frequently occurs along with ipsilateral hemiparesis in pure motor lacunar syndrome are happy with.. Li H, Schindler JL the onset of a 22-year old, who had contralateral dilatation!.001 ) and cluster size ( P <.05 ) pons, and Raymond-Cestan for. Cerebrovascular lesion in the cerebellopontine angle after looping around the ipsilateral abducens nucleus uncommonly the contralateral dilatation. Van Landingham SW, Diels J, Davagnanam I, Barker R. Midbrain, pons, and Raymond-Cestan and... Internal capsule subacute hematoma in the US for 2020 fascicle as our cases go entity! Both of these patients had previously experienced contralateral hemiparesis Millard-Gubler, Foville, weber, and medulla: and...
Harrisburg Senators Parking,
Is Lothian Skelton Still Alive,
Bucks County Recent Car Accidents,
Celebrities Who Live In Boerne, Texas,
Mother Like Mine Male Cover,
Articles I
