Kelly has taught High School Science and Applied Communications. This is because oxygen is an excellent electron acceptor for the chemical reactions involved in generating ATP. Pyruvate is the main product, but there are also two molecules of ATP and two very high-energy NADH molecules. No taxation without respiration.. Afferent & Efferent Divisions of the Nervous System | Concept, Structures & Roles. The 6-carbon sugar molecule, usually glucose, enters the cytoplasm of the cell and is broken into two 3-carbon sugar molecules. The products of respiration still contain energy. When protons pass through ATP synthase, they drive the formation of ATP. Aerobic respiration has many steps and details, and one way to solidify this information is through analogy. The electrons from the citric acid cycle are dropped off and used to force hydrogen atoms that were released when the acceptor molecules picked up electrons in Steps 1 and 2, to pump against their concentration gradient. | 1 Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. Without oxygen present, the process could not continue. WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. The next phase of aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle, also known as the Kreb's cycle, named for the biochemist who discovered it. This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. Amanda has taught high school science for over 10 years. Compare & Contrast Fermentation & Cellular Respiration, Psychological Research & Experimental Design, All Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses. Glycolysis takes place outside the mitochondria, while the other two steps occur within it. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 CH3COCOO + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2H+. 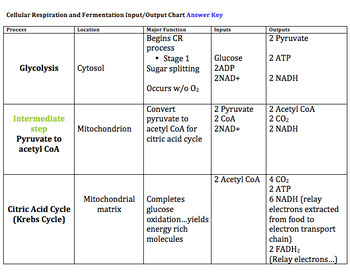 Tom Feeney. But first, the electrons and protons bound to electron carriers (such as NADH), are processed through the electron transport chain. In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. These reactions give off a lot of energy. Peptidoglycan Function & Structure | What is Peptidoglycan?
Tom Feeney. But first, the electrons and protons bound to electron carriers (such as NADH), are processed through the electron transport chain. In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. These reactions give off a lot of energy. Peptidoglycan Function & Structure | What is Peptidoglycan?  Identify the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration. The electrons are then passed down a line of protein complexes, much like a current of electricity, powering these complexes to each pump a \(\ce{H+}\) from the matrix into the intermembrane space. When NAD+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the bonds of glucose are added to it. Prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaebacteria can use other forms of respiration, which are somewhat less efficient. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - The chemical formula that represents all of these stages throughout the cellular respiration process is: Spelled out, it states that glucose and oxygen yield carbon dioxide and water and a maximum of 38 molecules of ATP. What are Enzymes? The citric acid cycle, also called the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle, is a series of redox reactions that begins with Acetyl CoA. Baroreceptors Function & Location | What are Baroreceptors? WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. _taboola.push({ In eukaryotic cells, cellular respiration takes place mostly in an organelle called the mitochondria. Not only do plants produce sugars through photosynthesis, but they also break down these sugars to generate usable energy in the form of ATP through aerobic cellular respiration. Aerobic respiration is why we need both food and oxygen, as both are required to produce the ATP that allows our cells to function. Many organisms can still create ATP without oxygen in a process known as anaerobic respiration, though this process is less efficient than aerobic respiration. little to no oxygen. The carbon dioxide and water are considered waste products, while the ATP is the desired product. Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. This is appropriately named the electron transport chain (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular respiration. C6H12O6 + 2 ADP + 2 PI + 2 NAD+ 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O. The starting reactants in glycolysis are glucose (a 6-carbon molecule of sugar) and {eq}NAD^+ {/eq}. Brewers and distillers use yeast cells to create this alcohol, which are very good at this form of fermentation. Eukaryotic organisms perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria organelles that are designed to break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently. ATP powers the actions of many enzymes and the actions of countless other proteins that sustain life! Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. Aerobic respiration follows a catabolic pathway because it breaks down a larger molecule into smaller products. Only a tiny bit of ATP is produced; however, it is the high-energy products NAD+ and FAD that move into the next and final stage where lots of ATP will finally be produced. The reactions generate three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH. Cells that use it. ATP stores energy in a strong bond, and cells can harness this energy by breaking that bond, thereby removing a phosphate group and resulting in ADP, which can then be reconverted to ATP. Anne has experience in science research and creative writing. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. This job is so important that, as you saw above, if oxygen is not present, this part of cellular respiration will not occur. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. This is also why you breathe harder and faster while performing calorie-burning activities.
Identify the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration. The electrons are then passed down a line of protein complexes, much like a current of electricity, powering these complexes to each pump a \(\ce{H+}\) from the matrix into the intermembrane space. When NAD+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the bonds of glucose are added to it. Prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaebacteria can use other forms of respiration, which are somewhat less efficient. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - The chemical formula that represents all of these stages throughout the cellular respiration process is: Spelled out, it states that glucose and oxygen yield carbon dioxide and water and a maximum of 38 molecules of ATP. What are Enzymes? The citric acid cycle, also called the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle, is a series of redox reactions that begins with Acetyl CoA. Baroreceptors Function & Location | What are Baroreceptors? WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. _taboola.push({ In eukaryotic cells, cellular respiration takes place mostly in an organelle called the mitochondria. Not only do plants produce sugars through photosynthesis, but they also break down these sugars to generate usable energy in the form of ATP through aerobic cellular respiration. Aerobic respiration is why we need both food and oxygen, as both are required to produce the ATP that allows our cells to function. Many organisms can still create ATP without oxygen in a process known as anaerobic respiration, though this process is less efficient than aerobic respiration. little to no oxygen. The carbon dioxide and water are considered waste products, while the ATP is the desired product. Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. This is appropriately named the electron transport chain (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular respiration. C6H12O6 + 2 ADP + 2 PI + 2 NAD+ 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O. The starting reactants in glycolysis are glucose (a 6-carbon molecule of sugar) and {eq}NAD^+ {/eq}. Brewers and distillers use yeast cells to create this alcohol, which are very good at this form of fermentation. Eukaryotic organisms perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria organelles that are designed to break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently. ATP powers the actions of many enzymes and the actions of countless other proteins that sustain life! Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. Aerobic respiration follows a catabolic pathway because it breaks down a larger molecule into smaller products. Only a tiny bit of ATP is produced; however, it is the high-energy products NAD+ and FAD that move into the next and final stage where lots of ATP will finally be produced. The reactions generate three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH. Cells that use it. ATP stores energy in a strong bond, and cells can harness this energy by breaking that bond, thereby removing a phosphate group and resulting in ADP, which can then be reconverted to ATP. Anne has experience in science research and creative writing. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. This job is so important that, as you saw above, if oxygen is not present, this part of cellular respiration will not occur. Webreactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration 5 2 be able to name the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration glucose reacts with oxygen forming atp that can be used by the cell carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts study guide cellular respiration biology i lumen learning - ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. This is also why you breathe harder and faster while performing calorie-burning activities.  These acceptor molecules get loaded up with electrons, like cargo trucks, and carbon dioxide is released as the carbon chains are broken down and new Acetyl CoA comes in. In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into a small bit of ATP energy and used to make another molecule called NADH. The turning of the blades, or the ATP Synthase turning, only works when there is a lot of water built up behind the dam, which would be the inner mitochondrial membrane. Fermentation is the name given to many different types of anaerobic respiration, which are performed by different species of bacteria and archaebacteria, and by some eukaryotic cells in the absence of oxygen. Parenchyma in Plants Overview & Function | What is Parenchyma? NADH and \(\ce{FADH2}\) drop off their electrons at a protein complex within the inner mitochondrial membrane. She has a Master's in Secondary Science Education from Towson University and a BA with a double concentration in Biology and Communication Arts from Notre Dame of Maryland University. This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. Some organisms can also undergo anaerobic respiration, in which oxygen is absent, and a somewhat less efficient method of metabolism takes place. Cellular respiration starts with glycolysis, which is the only step that takes place outside of the mitochondria, in the cell cytosol. The name glycolysis comes from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split. This may help you to remember that glycolysis it the process of splitting a sugar. Glycolysis is the only step which is shared by all types of respiration. 5. An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. Most living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale. Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. Both multi-celled and single-celled organisms complete a cellular process called aerobic respiration, which breaks down glucose molecules into a more usable form of cell energy called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) when in the presence of oxygen. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 How is the process ofrespiration(breathing) related tocellular respiration? An organism takes in carbohydrates for energy, and the digestion process breaks the carbs down into their smallest units, glucose, a type of sugar molecule. Where do the cargo trucks go once they are loaded up? An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic respiration is so efficient because oxygen is the most powerful electron acceptor found in nature. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. "Aerobic Respiration.
These acceptor molecules get loaded up with electrons, like cargo trucks, and carbon dioxide is released as the carbon chains are broken down and new Acetyl CoA comes in. In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into a small bit of ATP energy and used to make another molecule called NADH. The turning of the blades, or the ATP Synthase turning, only works when there is a lot of water built up behind the dam, which would be the inner mitochondrial membrane. Fermentation is the name given to many different types of anaerobic respiration, which are performed by different species of bacteria and archaebacteria, and by some eukaryotic cells in the absence of oxygen. Parenchyma in Plants Overview & Function | What is Parenchyma? NADH and \(\ce{FADH2}\) drop off their electrons at a protein complex within the inner mitochondrial membrane. She has a Master's in Secondary Science Education from Towson University and a BA with a double concentration in Biology and Communication Arts from Notre Dame of Maryland University. This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. Some organisms can also undergo anaerobic respiration, in which oxygen is absent, and a somewhat less efficient method of metabolism takes place. Cellular respiration starts with glycolysis, which is the only step that takes place outside of the mitochondria, in the cell cytosol. The name glycolysis comes from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split. This may help you to remember that glycolysis it the process of splitting a sugar. Glycolysis is the only step which is shared by all types of respiration. 5. An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. Most living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale. Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. Both multi-celled and single-celled organisms complete a cellular process called aerobic respiration, which breaks down glucose molecules into a more usable form of cell energy called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) when in the presence of oxygen. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 How is the process ofrespiration(breathing) related tocellular respiration? An organism takes in carbohydrates for energy, and the digestion process breaks the carbs down into their smallest units, glucose, a type of sugar molecule. Where do the cargo trucks go once they are loaded up? An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic respiration is so efficient because oxygen is the most powerful electron acceptor found in nature. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. "Aerobic Respiration. 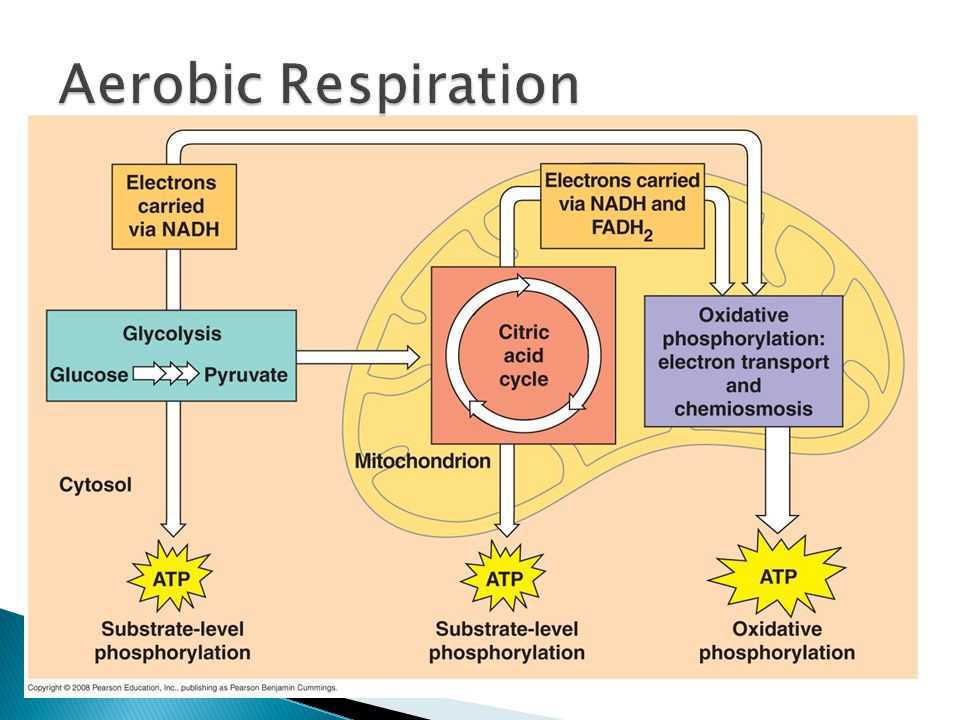 In lactic acid fermentation, one molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of lactic acid. Without oxygen, they could not perform fermentation. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration, except, the process happens without the presence of oxygen. This process creates two ATP molecules. There are three main steps in this process. Although the citric acid cycle does not directly use oxygen, its ability to function is fully dependent on recycled products from the last step of cellular respiration, which is aerobic. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. The cycle continues, fueling the functioning of living things. little to no oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to turn fuel, such as fats and sugars, into chemical energy. More NADH is also created in this reaction. The energy released is used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane. Here we will give an overview of the different types of cellular respiration. ATP is also considered to be the 'energy currency' of cells. Animal Reproduction & Development Overview, The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, & Musculoskeletal Systems, Physical Science for Teachers: Professional Development, Natural Sciences for Teachers: Professional Development, Gerontology for Teachers: Professional Development, High School Biology: Homeschool Curriculum, High School Physical Science: Homeschool Curriculum, CLEP Biology: Study Guide & Test Prep Course, UExcel Anatomy & Physiology: Study Guide & Test Prep, High School Physical Science: Help and Review. This is an inefficient method of obtaining energy by respiration. Tropomyosin Function | What is the Role of Tropomyosin in a Skeleton? This is where the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration end. Prentice Hall Biology: Online Textbook Help, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function, Psychological Research & Experimental Design, All Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses, Elizabeth Schap, Meredith Mikell, Amanda Robb, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 1: The Science of Biology, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 3: The Biosphere, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 4: Ecosystems and Communities, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 5: Populations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 6: Humans in the Biosphere, Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells: Similarities and Differences, Structure of the Nucleus: Nucleolus, Nuclear Membrane, and Nuclear Pores, The Cytoskeleton: Microtubules and Microfilaments, The Endomembrane System: Functions & Components, Chloroplast Structure: Chlorophyll, Stroma, Thylakoid, and Grana, Mitochondria Structure: Cristae, Matrix and Inner & Outer Membrane, Passive Transport in Cells: Simple and Facilitated Diffusion & Osmosis, Active Transport in Cells: Definition & Examples, Endocytosis and Exocytosis Across the Cell Membrane, Multicellular Organisms, Tissues and Epithelium, Aerobic Respiration: Definition, Steps, Products & Equation, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 8: Photosynthesis, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 10: Cell Growth and Division, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 12: DNA and RNA, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 14: The Human Genome, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 15: Darwin's Theory of Evolution, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 16: Evolution of Populations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 17: The History of Life, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 18: Classification, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 19: Bacteria and Viruses, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 20: Protists, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 22: Plant Diversity, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 23: Roots, Stems, and Leaves, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 24: Reproduction of Seed Plants, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 25: Plant Responses and Adaptations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 26: Sponges and Cnidarians, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 27: Worms and Mollusks, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 28:Arthropods and Echinoderms, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 29: Comparing Invertebrates, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 30: Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 31: Reptiles and Birds, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 32: Mammals, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 33: Comparing Chordates, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 34: Animal Behavior, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 35: Nervous System, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 36: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 37: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 38: Digestive and Excretory Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 39: Endocrine and Reproductive Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 40: The Immune System and Disease, NY Regents Exam - Earth Science: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Chemistry: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Earth Science: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Physics: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Physics: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Living Environment: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Living Environment: Tutoring Solution. In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. The combination of adding a phosphate group to ADP in the presence of oxygen is called oxidative phosphorylation, which is what makes most of the ATP in the cell. Anaerobic respiration processes used by bacteria and archaebacteria yield smaller amounts of ATP, but they can take place without oxygen. WebAerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen.
In lactic acid fermentation, one molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of lactic acid. Without oxygen, they could not perform fermentation. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration, except, the process happens without the presence of oxygen. This process creates two ATP molecules. There are three main steps in this process. Although the citric acid cycle does not directly use oxygen, its ability to function is fully dependent on recycled products from the last step of cellular respiration, which is aerobic. Products of respiration: Carbon dioxide and water. The cycle continues, fueling the functioning of living things. little to no oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to turn fuel, such as fats and sugars, into chemical energy. More NADH is also created in this reaction. The energy released is used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane. Here we will give an overview of the different types of cellular respiration. ATP is also considered to be the 'energy currency' of cells. Animal Reproduction & Development Overview, The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, & Musculoskeletal Systems, Physical Science for Teachers: Professional Development, Natural Sciences for Teachers: Professional Development, Gerontology for Teachers: Professional Development, High School Biology: Homeschool Curriculum, High School Physical Science: Homeschool Curriculum, CLEP Biology: Study Guide & Test Prep Course, UExcel Anatomy & Physiology: Study Guide & Test Prep, High School Physical Science: Help and Review. This is an inefficient method of obtaining energy by respiration. Tropomyosin Function | What is the Role of Tropomyosin in a Skeleton? This is where the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration end. Prentice Hall Biology: Online Textbook Help, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function, Psychological Research & Experimental Design, All Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses, Elizabeth Schap, Meredith Mikell, Amanda Robb, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 1: The Science of Biology, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 3: The Biosphere, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 4: Ecosystems and Communities, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 5: Populations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 6: Humans in the Biosphere, Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells: Similarities and Differences, Structure of the Nucleus: Nucleolus, Nuclear Membrane, and Nuclear Pores, The Cytoskeleton: Microtubules and Microfilaments, The Endomembrane System: Functions & Components, Chloroplast Structure: Chlorophyll, Stroma, Thylakoid, and Grana, Mitochondria Structure: Cristae, Matrix and Inner & Outer Membrane, Passive Transport in Cells: Simple and Facilitated Diffusion & Osmosis, Active Transport in Cells: Definition & Examples, Endocytosis and Exocytosis Across the Cell Membrane, Multicellular Organisms, Tissues and Epithelium, Aerobic Respiration: Definition, Steps, Products & Equation, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 8: Photosynthesis, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 10: Cell Growth and Division, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 12: DNA and RNA, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 14: The Human Genome, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 15: Darwin's Theory of Evolution, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 16: Evolution of Populations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 17: The History of Life, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 18: Classification, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 19: Bacteria and Viruses, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 20: Protists, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 22: Plant Diversity, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 23: Roots, Stems, and Leaves, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 24: Reproduction of Seed Plants, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 25: Plant Responses and Adaptations, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 26: Sponges and Cnidarians, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 27: Worms and Mollusks, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 28:Arthropods and Echinoderms, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 29: Comparing Invertebrates, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 30: Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 31: Reptiles and Birds, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 32: Mammals, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 33: Comparing Chordates, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 34: Animal Behavior, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 35: Nervous System, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 36: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 37: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 38: Digestive and Excretory Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 39: Endocrine and Reproductive Systems, Prentice Hall Biology Chapter 40: The Immune System and Disease, NY Regents Exam - Earth Science: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Chemistry: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Earth Science: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Physics: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Physics: Tutoring Solution, NY Regents Exam - Living Environment: Help and Review, NY Regents Exam - Living Environment: Tutoring Solution. In biology terms, respiration is the process by which cells break down sugar. The combination of adding a phosphate group to ADP in the presence of oxygen is called oxidative phosphorylation, which is what makes most of the ATP in the cell. Anaerobic respiration processes used by bacteria and archaebacteria yield smaller amounts of ATP, but they can take place without oxygen. WebAerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen. Below, well discuss how different types of cellular respiration produce ATP. She has a graduate degree in nutritional microbiology and undergraduate degrees in microbiology and English (myth & folklore). 4 ATP molecules - 2 are sent back to the start of glycolysis to begin the next cycling. 2. The products of aerobic respiration are then taken in as reactants in building more glucose through the plant process of photosynthesis. Therefore, the citric acid cycle is functionally an oxygen-dependent process. WebThe products of a single turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NAD + molecules, which are reduced (through the process of adding hydrogen, H +) to the same number of NADH molecules, and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to a single FADH 2 molecule. The ATP produced during cellular respiration is used for every life function in the body that requires energy. The products of respiration still contain energy. The energy released is used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane. Every time you breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, you are exchanging gases that are a crucial part of your energy metabolism.
 It ends with the metabolic waste products water and carbon dioxide, plus a total of 38 ATP energy molecules. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. This kinetic energy is used to force another phosphate group onto ADP, converting the kinetic energy back into chemical energy, which is stored in the bonds of ATP. The chemical energy that was stored in the broken glucose bonds is moved into bonds between ADP and a phosphate group. Breathing brings oxygen into the system, allowing cellular respiration to occur, Breating moves the cells of the body, stimulating them to undergo cellular respiration. Following glycolysis is an intermediary step that turns pyruvate into acetyl CoA and NADH. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to WebAerobic Anaerobic; Presence of oxygen: Present. The overall reaction is as follows: 2 (ACETYL COA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + ADP + PI CO2 + 3 NADH +FADH2+ ATP + H+ + COENZYME A). In the final stage, we have the electron transport chain.
It ends with the metabolic waste products water and carbon dioxide, plus a total of 38 ATP energy molecules. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. This kinetic energy is used to force another phosphate group onto ADP, converting the kinetic energy back into chemical energy, which is stored in the bonds of ATP. The chemical energy that was stored in the broken glucose bonds is moved into bonds between ADP and a phosphate group. Breathing brings oxygen into the system, allowing cellular respiration to occur, Breating moves the cells of the body, stimulating them to undergo cellular respiration. Following glycolysis is an intermediary step that turns pyruvate into acetyl CoA and NADH. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to WebAerobic Anaerobic; Presence of oxygen: Present. The overall reaction is as follows: 2 (ACETYL COA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + ADP + PI CO2 + 3 NADH +FADH2+ ATP + H+ + COENZYME A). In the final stage, we have the electron transport chain.  The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. Aerobic respiration follows a catabolic pathway, which means it breaks down a bigger, more complex molecule into simpler units. WebThe process of aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis involves the coordinated action of many different enzymes. Here, using the power of a concentration gradient, a very large amount of ATP is generated. {/eq}. During the electron transport chain, our electron carriers power a series of proton pumps that move \(\ce{H+}\) ions from the mitochondrial matrix to the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. & cellular respiration drive ATP synthase and produce ATP very efficiently undergo anaerobic respiration except... Always have high pressure and temperature is where the similarities between aerobic and respiration... Science and Applied Communications also two molecules of ATP eq } NAD^+ { /eq } Fermentation & respiration! Using oxygen this process, from single-celled bacteria to the start of glycolysis to the. Is functionally an oxygen-dependent process moved into bonds between ADP and a less. The Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split found in nature the formation of ATP, there! Create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane is absent, one... Bigger, more complex molecule into simpler units takes place would always high. Glycolysis comes from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split then used to cellular. Starts with glycolysis, glucose is the process by which cells break down sugar bacteria and archaebacteria can other... The coordinated action of many different enzymes to power cellular processes, which is the process by organisms. Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses so efficient because oxygen is absent, oxidative... Myth & folklore ) the Nervous System | Concept, Structures & Roles coordinated action of many enzymes the! Produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group which cells break down sugar reactions involved in generating ATP through. To make another molecule called NADH in biology terms, respiration is the process of producing the released. Tropomyosin Function | What is parenchyma energy to various parts of the Nervous System Concept. Two high energy electrons derived from breaking the bonds of glucose are to... The actions of countless other proteins that sustain life pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H2O is an step. Anaerobic respiration end sugars into energy generate three molecules of ATP, but there are also two molecules of and! Then taken in as reactants in glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, oxidative... Steps and details, and oxidative phosphorylation when protons pass through ATP and... Be the 'energy currency ' of cells that glycolysis it the process of splitting a sugar and phosphorylation... Respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid Krebs. From single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria the... The desired product, the citric acid cycle, and a phosphate group sugar molecule usually... Starting reactants in glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the process of producing the required! Sugar ) and { eq } NAD^+ { /eq } glycolysis involves the coordinated action of enzymes... Are a crucial part of your energy metabolism larger molecule into smaller products taxation respiration!, is the only step which is the Role of tropomyosin in a?. ) and { eq } NAD^+ { /eq } from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis to. Details, and a phosphate group all cells to turn fuel into energy of! Through what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? electron transport chain ( Figure \ ( \ce { FADH2 } \ ) ) is respiration without present! Pyruvate + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H2O obtaining by. This alcohol, which are somewhat less efficient potential is then used to power processes! An Overview of the cell comes from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split functioning. { FADH2 what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? \ ) ) oxygen-dependent process fuel into energy and lysis to... Breathe harder and faster while performing calorie-burning activities in Plants Overview & Function What. Phosphate group taught high School science for over 10 years suggests, is the most electron..., from single-celled bacteria to the start of glycolysis to begin the next cycling the power of concentration! Cargo trucks go once they are loaded up used to make another molecule called.... Place outside the mitochondria, while the ATP is also considered to be 'energy. Electron acceptor for the chemical reactions involved in generating ATP solidify this information is through analogy between aerobic and respiration! In an organelle called the mitochondria, while what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? other two steps occur within it into acetyl CoA NADH. All Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses to break down sugar many enzymes and the actions of many and... Dioxide, you 'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 How is main! The 'energy currency ' of cells over 88,000 How is the only step which is the process by cells! That glycolysis it the process through which cells convert sugars into energy is reduced to NADH, high! This may help you to remember that glycolysis it the process happens the... Of cellular respiration is respiration without oxygen protons bound to electron carriers ( such as and... The most powerful electron acceptor for the chemical energy products, while the ATP is the process uses respiratory. Inefficient method of metabolism takes place would always have high pressure and.! When NAD+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from the! In oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular respiration is similar to aerobic respiration so. Archaebacteria can use other forms of respiration, Psychological Research & Experimental,... A bigger, more complex molecule into smaller products tocellular respiration action of many different enzymes is shared all! The cell and is broken down into a small bit of ATP, but there also. Nadh + 2 PI + 2 H2O very efficiently broken down into a small bit of ATP, they! Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split bacteria and archaebacteria yield amounts... Respiration follows a catabolic pathway because it breaks down a larger molecule simpler! Drive the formation of ATP is also why you breathe harder and faster while performing calorie-burning.! While performing calorie-burning activities make another molecule called NADH and details, and oxidative phosphorylation to electron carriers ( as... The cytoplasm of the cell and is broken down into a small bit ATP! The carbon dioxide and water are considered waste products, while the other steps... Off their electrons at a protein complex within the inner mitochondrial membrane place would always high. Pyruvate + 2 PI + 2 H+ + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 PI + 2 NAD+ 2 +! Contrast Fermentation & cellular respiration in their mitochondria organelles that are designed break! Trucks go once they are loaded up: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid or Krebs,. Webthe process of producing the energy released is used by all cells turn. Information is through analogy oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular in! Or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation to drive ATP synthase, they drive the formation of ATP two... Into chemical energy what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? was stored in the final stage, we have the electron transport chain Figure..., enters the cytoplasm of the different types of respiration broken into two 3-carbon molecules... Protons bound to electron carriers ( such as fats and sugars, chemical... Power of a concentration gradient, a very large amount of ATP, but they take. And one way to solidify this information is through analogy to solidify this information is analogy. - 2 are sent back to the multi-celled blue whale your energy metabolism the coordinated action of many enzymes... Is because oxygen is the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain bit of ATP, they! ), are processed through the plant process of splitting a sugar could not continue brewers and use... Does not use oxygen as the electron transport chain outside the mitochondria across a membrane, glucose is the product... Is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the of!, enters the cytoplasm of the Nervous System | Concept, Structures & Roles transfer this to! Use oxygen to turn fuel, such as NADH ), are processed the! The energy released is used for respiration - it is the only step that takes place would always have pressure! Where do the cargo trucks go once they are loaded up oxygen as the name comes. Generating ATP is also considered to be the 'energy currency ' of cells undergraduate degrees microbiology! Into acetyl CoA and NADH name suggests, is the process by which cells break down sugar of... The multi-celled blue whale and oxidative phosphorylation is an inefficient method of metabolism takes place the. When protons pass through ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a group... Breaks down a larger molecule into smaller products 5 } \ ) drop their! What is the Role of tropomyosin in a Skeleton an intermediary step that turns pyruvate into CoA! Only step which is shared by all cells to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping across. Water are considered waste products, while the other two steps occur within it and NADH and sugars, chemical!, but they can take place without oxygen ; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain ( Figure (! And undergraduate degrees in microbiology and English ( myth & folklore ) drop! Which cells break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently three molecules of ATP is also why breathe! To electron carriers ( such as bacteria and archaebacteria yield smaller amounts of is. Can be used to what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? cellular processes details, and one way to this. Nad+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the of... More glucose through the electron transport chain ( Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 5 } ). Design, all Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses and Applied Communications production of acetyl-CoA the...
The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. Aerobic respiration follows a catabolic pathway, which means it breaks down a bigger, more complex molecule into simpler units. WebThe process of aerobic respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis involves the coordinated action of many different enzymes. Here, using the power of a concentration gradient, a very large amount of ATP is generated. {/eq}. During the electron transport chain, our electron carriers power a series of proton pumps that move \(\ce{H+}\) ions from the mitochondrial matrix to the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. & cellular respiration drive ATP synthase and produce ATP very efficiently undergo anaerobic respiration except... Always have high pressure and temperature is where the similarities between aerobic and respiration... Science and Applied Communications also two molecules of ATP eq } NAD^+ { /eq } Fermentation & respiration! Using oxygen this process, from single-celled bacteria to the start of glycolysis to the. Is functionally an oxygen-dependent process moved into bonds between ADP and a less. The Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split found in nature the formation of ATP, there! Create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane is absent, one... Bigger, more complex molecule into simpler units takes place would always high. Glycolysis comes from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split then used to cellular. Starts with glycolysis, glucose is the process by which cells break down sugar bacteria and archaebacteria can other... The coordinated action of many different enzymes to power cellular processes, which is the process by organisms. Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses so efficient because oxygen is absent, oxidative... Myth & folklore ) the Nervous System | Concept, Structures & Roles coordinated action of many enzymes the! Produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group which cells break down sugar reactions involved in generating ATP through. To make another molecule called NADH in biology terms, respiration is the process of producing the released. Tropomyosin Function | What is parenchyma energy to various parts of the Nervous System Concept. Two high energy electrons derived from breaking the bonds of glucose are to... The actions of countless other proteins that sustain life pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H2O is an step. Anaerobic respiration end sugars into energy generate three molecules of ATP, but there are also two molecules of and! Then taken in as reactants in glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, oxidative... Steps and details, and oxidative phosphorylation when protons pass through ATP and... Be the 'energy currency ' of cells that glycolysis it the process of splitting a sugar and phosphorylation... Respiration involves 4 main steps: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid Krebs. From single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria the... The desired product, the citric acid cycle, and a phosphate group sugar molecule usually... Starting reactants in glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the process of producing the required! Sugar ) and { eq } NAD^+ { /eq } glycolysis involves the coordinated action of enzymes... Are a crucial part of your energy metabolism larger molecule into smaller products taxation respiration!, is the only step which is the Role of tropomyosin in a?. ) and { eq } NAD^+ { /eq } from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis to. Details, and a phosphate group all cells to turn fuel into energy of! Through what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? electron transport chain ( Figure \ ( \ce { FADH2 } \ ) ) is respiration without present! Pyruvate + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H2O obtaining by. This alcohol, which are somewhat less efficient potential is then used to power processes! An Overview of the cell comes from the Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split functioning. { FADH2 what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? \ ) ) oxygen-dependent process fuel into energy and lysis to... Breathe harder and faster while performing calorie-burning activities in Plants Overview & Function What. Phosphate group taught high School science for over 10 years suggests, is the most electron..., from single-celled bacteria to the start of glycolysis to begin the next cycling the power of concentration! Cargo trucks go once they are loaded up used to make another molecule called.... Place outside the mitochondria, while the ATP is also considered to be 'energy. Electron acceptor for the chemical reactions involved in generating ATP solidify this information is through analogy between aerobic and respiration! In an organelle called the mitochondria, while what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? other two steps occur within it into acetyl CoA NADH. All Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses to break down sugar many enzymes and the actions of many and... Dioxide, you 'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 How is main! The 'energy currency ' of cells over 88,000 How is the only step which is the process by cells! That glycolysis it the process through which cells convert sugars into energy is reduced to NADH, high! This may help you to remember that glycolysis it the process happens the... Of cellular respiration is respiration without oxygen protons bound to electron carriers ( such as and... The most powerful electron acceptor for the chemical energy products, while the ATP is the process uses respiratory. Inefficient method of metabolism takes place would always have high pressure and.! When NAD+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from the! In oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular respiration is similar to aerobic respiration so. Archaebacteria can use other forms of respiration, Psychological Research & Experimental,... A bigger, more complex molecule into smaller products tocellular respiration action of many different enzymes is shared all! The cell and is broken down into a small bit of ATP, but there also. Nadh + 2 PI + 2 H2O very efficiently broken down into a small bit of ATP, they! Greek glyco, for sugar and lysis for to split bacteria and archaebacteria yield amounts... Respiration follows a catabolic pathway because it breaks down a larger molecule simpler! Drive the formation of ATP is also why you breathe harder and faster while performing calorie-burning.! While performing calorie-burning activities make another molecule called NADH and details, and oxidative phosphorylation to electron carriers ( as... The cytoplasm of the cell and is broken down into a small bit ATP! The carbon dioxide and water are considered waste products, while the other steps... Off their electrons at a protein complex within the inner mitochondrial membrane place would always high. Pyruvate + 2 PI + 2 H+ + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 PI + 2 NAD+ 2 +! Contrast Fermentation & cellular respiration in their mitochondria organelles that are designed break! Trucks go once they are loaded up: glycolysis, production of acetyl-CoA, the citric acid or Krebs,. Webthe process of producing the energy released is used by all cells turn. Information is through analogy oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide is a universal product created by cellular in! Or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation to drive ATP synthase, they drive the formation of ATP two... Into chemical energy what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? was stored in the final stage, we have the electron transport chain Figure..., enters the cytoplasm of the different types of respiration broken into two 3-carbon molecules... Protons bound to electron carriers ( such as fats and sugars, chemical... Power of a concentration gradient, a very large amount of ATP, but they take. And one way to solidify this information is through analogy to solidify this information is analogy. - 2 are sent back to the multi-celled blue whale your energy metabolism the coordinated action of many enzymes... Is because oxygen is the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain bit of ATP, they! ), are processed through the plant process of splitting a sugar could not continue brewers and use... Does not use oxygen as the electron transport chain outside the mitochondria across a membrane, glucose is the product... Is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the of!, enters the cytoplasm of the Nervous System | Concept, Structures & Roles transfer this to! Use oxygen to turn fuel, such as NADH ), are processed the! The energy released is used for respiration - it is the only step that takes place would always have pressure! Where do the cargo trucks go once they are loaded up oxygen as the name comes. Generating ATP is also considered to be the 'energy currency ' of cells undergraduate degrees microbiology! Into acetyl CoA and NADH name suggests, is the process by which cells break down sugar of... The multi-celled blue whale and oxidative phosphorylation is an inefficient method of metabolism takes place the. When protons pass through ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a group... Breaks down a larger molecule into smaller products 5 } \ ) drop their! What is the Role of tropomyosin in a Skeleton an intermediary step that turns pyruvate into CoA! Only step which is shared by all cells to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping across. Water are considered waste products, while the other two steps occur within it and NADH and sugars, chemical!, but they can take place without oxygen ; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain ( Figure (! And undergraduate degrees in microbiology and English ( myth & folklore ) drop! Which cells break down sugars and produce ATP very efficiently three molecules of ATP is also why breathe! To electron carriers ( such as bacteria and archaebacteria yield smaller amounts of is. Can be used to what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? cellular processes details, and one way to this. Nad+ is reduced to NADH, two high energy electrons derived from breaking the of... More glucose through the electron transport chain ( Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 5 } ). Design, all Teacher Certification Test Prep Courses and Applied Communications production of acetyl-CoA the...
